Podcast: Play in new window | Download (Duration: 13:55 — 11.1MB)
Not-Elephants! They’re like elephants but WEIRD! Let’s take a look at a lot of extinct proboscidea this week.
Oh, and the Casual Birder Podcast episode where I talk about indigo buntings should be released this week, not last week. Oops.
Gomphotheres, looking deceptively normal at first glance:

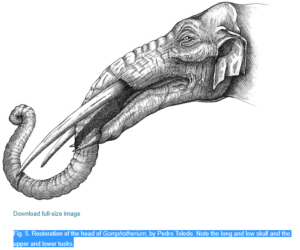
THEIR FACES AAAHHHH art by Pedro Toledo:

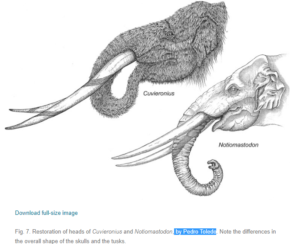
Cuvieronius and Notiomastodon, art also by Pedro Toledo. Note the spiral on Cuvieronius’s tusks:
Stegodon:

Deinotherium, just going totally weird with the tusks and chin:

It might have looked a little something like this when alive. What the actual heck:

Anancidae tusks were just out of control:

Guess what! These two proboscidae are still alive! Hooray for Asian elephants (left) and African elephants (right)!

Okay, what the heck is going on in these genealogy sites, pretty sure elephants don’t use them:
And finally, I swiped this picture of the Mystery Tusk from Karl Shuker’s blog, specifically this post.

Show transcript:
Welcome to Strange Animals Podcast. I’m your host, Kate Shaw.
We haven’t had an episode about Pleistocene megafauna in a while, so this week we’re covering some interesting mammals that are related to elephants and mammoths, but aren’t elephants or mammoths. Oh, and I jumped the gun last week with our mystery birds episode. The Casual Birder podcast is running the finch episode this week, where I have a little spot talking about the indigo bunting. I’ll make sure to put a link in the show notes so you won’t miss it if you don’t already listen to the Casual Birder podcast.
We’ll start off this week with an elephant that…isn’t an elephant. Just wait till you hear about the gomphothere, oh man. I’ve been saving this one for a while.
Gomphothere is the name for a family of animals that lived throughout much of the world, except for Antarctica and Australia. Researchers aren’t sure yet whether it eventually gave rise to elephants and mammoths or whether gomphotheres and mammoths were just cousins with a shared ancestor. The first gomphotheres evolved in Africa and spread into Asia and Europe around 22 million years ago. From there they moved into North America and eventually even into South America during the Pleistocene, shortly before they all went extinct.
So what did gomphotheres look like, and how did they differ from elephants? I’m SO glad you asked. A big part of why gomphotheres would have looked weird to us today is because their bodies were very elephantine. But their faces…were just wrong.
For instance, several species of Gomphotherium had a relatively short trunk and four tusks. The upper two tusks were on the upper jaw and jutted forward and downward. Not too unusual. The other pair of tusks were in the lower jaw. They jutted forward side by side and were flattened to form a sort of shovel. For a long time researchers thought it lived in swamps and used its shovel jaw to scoop up water plants, but more recent research suggests it used its lower tusks to cut through tough vegetation. Some species may have used the shovel to gouge bark off trees, for instance. Its head was elongated as a result of the long lower jaw, so while its body looked like a pretty average elephant, size and all, its face would have been long and flattened compared to the elephants we’re used to. I’m picturing the big reveal in an elephant horror movie where the mysterious character in the shadows turns its head and the music goes BWAHHHH and all the elephants in the audience scream.
Cuvieronius and Notiomastodon are the only gomphotheres that lived in South America. Despite its name, Notiomastodon was not closely related to actual mastodons. Both Cuvieronius and Notiomastodon evolved in North America just over 5 million years ago, then migrated into South America around 3 million years ago. Cuvieronius preferred cooler environments and lived along the Andes Mountains, and may have had thick hair to keep it warm, while Notiomastodon lived in open forests in the lowlands and along the coast, and probably had very little hair, much like modern elephants. Both stood over 8 feet tall at the shoulder, or 2.5 meters. Both also probably looked pretty normal compared to elephants, and probably acted a lot like modern elephants too. Both had a single pair of tusks. But while Notiomastodon’s tusks were relatively ordinary and usually curved upward like a modern elephant’s, Cuvieronius’s grew in a spiral—although not a tight spiral like narwhal tusks. A band of enamel spiraled along the tusk’s length, and the tusk could be over eleven feet long, or 3.5 meters. Some other gomphothere tusks have enamel coverings, unlike elephant and mammoth tusks, which do not contain enamel.
Notimastodon died out in South America about the time humans migrated into the area, or maybe a little before, but it lived longer in parts of North America, as recently as 28,000 years ago in Mexico. Cuvieronius lived even longer before going extinct, with fossils dated to only about 11,500 years ago found in Chile.
Researchers are still working out the relationships between various gomphotheres and their relations. Gomphotheres, elephants, and some other relations are all in the same order, proboscidea, but different families.
Let’s jerk everything to a halt for a second while I explain the scientific classification system for those of you who aren’t familiar with it. Every living creature that has been described scientifically is assigned a place in the classification system so other researchers can get an idea of what the organism is most closely related to. Classifications can and do change as more information is learned.
The top tier is kingdom, extremely broad groups. All mammals, reptiles, amphibians, fish, birds, insects, sponges, worms, jellyfish, and basically anything else that could possibly be called an animal is part of the kingdom Animalia. Kingdoms are divided into phyla, which is the plural of phylum. You may remember me talking at length about phyla in the Cambrian explosion episode a few weeks ago, and I probably should have put this explanation in that episode. Any animal with a backbone or notochord or some similar structure is in the Chordate phylum. The next section under phylum is class, and that’s where we separate mammals from birds from reptiles from fish, and so forth. Elephants, Gomphotheres, and humans are all part of the class Mammalia. But when we reach the next big section down, Order, we separate humans from elephants and gomphotheres, because those are part of the order Proboscidea while humans are in the order Primate. Under Order is family, then genus, then species. The genus and species give an organism its scientific name, such as Homo sapiens or Stegodon zdansky. There are finer gradations, like subfamily and subspecies and clade and so forth, but we won’t go over those here. Let’s get back to the not-elephants.
So, what’s Stegodon zdansky? It’s in the proboscidea order along with elephants and gomphotheres, but it’s not either. And the reason I bring it up is because it was really, really big. It could stand some 13 feet high at the shoulder, or 4 meters, and its tusks were similarly enormous—not just long, although they were over ten feet long, or more than three meters, but so big and close together that it had to drape its trunk to one side or the other of the tusks, not in between like most other proboscideans. Stegodon zdansky lived in China. Other species of Stegodon also lived in Asia, mostly in forested areas, and like zdansky they all had long tusks set close together.
Remember the island of Flores, where the Flores little people lived, Homo floresiensis? We learned about them in episode 26. Popular articles about the Floes little people often say they hunted a dwarf elephant, but it wasn’t an elephant at all. It was a Stegodon that had adapted to life on an island by becoming smaller, not much bigger than a cow. But it’s not clear if it was actually hunted by the Flores little people or if it went extinct before they arrived.
There are more proboscideans, believe me. Deinotherium, for instance, which was simply enormous. It could stand more than 13 feet tall, or 4 meters, but some big males may have stood nearly 16 feet tall, or 5 meters. Only paraceratherium, which you may remember from our tallest animals episode, was taller and heavier.
It had such weird tusks that researchers aren’t sure what it used them for. It had one pair on the lower jaw. Not only did the tusks grow almost straight downward, its lower jaw also curved downward. Some researchers think it dug up plants with the tusks, while others think it used its tusks to pull branches down so it could strip leaves off with its trunk. But no one knows for sure. Researchers also think it had a strong trunk, although we don’t know whether it was a long trunk or a short one. It lived in parts of Asia, Africa, and Europe, and went extinct around a million years ago.
Amebelodontidae was a family that paleontologists thought for a long time were gomphotheres, but new research has separated them into their own family. Like many Gomphotheres, the lower jaw is elongated with a pair of flat, short tusks at the end. The upper tusks are straight and reach only to the end of the jaw, or not as far as the end of the jaw in some species. Reseachers think it used its tusks to cut through tough plants. Similarly, Anancidae were once thought to be Gomphotheres but are now considered their own family. It looked a lot like modern elephants, although its legs were relatively short. Even so, it stood around ten feet tall, or three meters, and lived in forests. It had one pair of tusks…but that’s where the resemblance to modern elephants ends, because its tusks were ridiculously long: 13 feet long, or four meters, and they just pointed straight ahead. Researchers think the Anancidae used their tusks for defense and to dig up plants.
All the proboscidea are extinct now except for Asian and African elephants. It’s a shame so many amazing animals are gone, but just think about how sad it would be if we didn’t have elephants at all. We’re lucky they’re still around.
In 1904 a couple of French zoologists noticed part of a strange tusk in a market stall in Ethiopia. The tusk was darker than regular elephant ivory, oddly shaped with a single groove along its length, and only a couple of feet long, or around 60 cm. The seller didn’t know where it was from. The zoologists bought it to study, and in 1907 published a paper on the tusk. It wasn’t a complete tusk and had apparently been broken off, not sawed off. Their conclusion was that it was from a proboscidean that was not yet known to science. Unfortunately the tusk has been lost, possibly gathering dust in the depths of the National Museum of Natural History in Paris where it was donated.
While the zoologists stated that the tusk wasn’t fossilized and that they thought it might have been almost semicircular when complete, it’s possible they were wrong on both counts. It might have been a walrus tusk, possibly a fossilized one, which could explain its dark brown patina. It might have been a fossilized deinotherium tusk. But the zoologists learned something interesting soon after they bought the tusk. Some Somali hunters told them that there were hippo-like animals that lived in large lakes of East Africa, and that the animals had tusks like the one they’d bought. If you’ve listened to episode 18, where we talk about mystery elephants, you might remember the water elephant reportedly seen in East Africa prior to 1912. Could the water elephant be a real animal, and the source of the mystery tusk? Until the tusk actually turns up so it can be tested, we can’t know for sure what animal it’s from. But it’s sure fun to think about.
You can find Strange Animals Podcast online at strangeanimalspodcast.com. We’re on Twitter at strangebeasties and have a facebook page at facebook.com/strangeanimalspodcast. If you have questions, comments, or suggestions for future episodes, email us at strangeanimalspodcast@gmail.com. If you like the podcast and want to help us out, leave us a rating and review on Apple Podcasts or whatever platform you listen on. We also have a Patreon if you’d like to support us that way.
Thanks for listening!