Podcast: Play in new window | Download (Duration: 11:38 — 11.7MB)
It’s time to learn about some more dinosaurs, ceratopsids, including the well-known Triceratops!
Triceratops:

An artist’s frankly awesome rendition of Sinoceratops. I love it:

A Kosmoceratops skull:


Pachyrhinosaurus had a massive snoot:


Protoceratops:


Fighting dinos!


Show transcript:
Welcome to Strange Animals Podcast. I’m your host, Kate Shaw.
Back in episode 107, about ankylosaurus and stegosaurus, I mentioned that one day I’d do an episode all about triceratops and its relations. Well, that day is today. It’s the ceratopsid episode!
Ceratopsids are a family of dinosaurs with elaborate horns on their faces and frills on the back of their heads. They almost all lived in what is now North America and most of them lived in the late Cretaceous. Triceratops is the most well known, so we’ll start with it.
The name triceratops, of course, means three face horns, and it did indeed have three face horns. It had one on its nose and two on its brow, plus a frill that projected from the back of its skull.
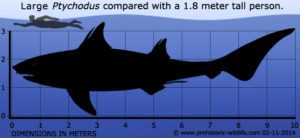
Triceratops was a big animal, around 10 feet high at the shoulder, or 3 meters, and about 30 feet long, or 9 meters. Its body was bulky and heavy, sort of like a rhinoceros but, you know, even bigger and more terrifying.
Like the rhinoceros, triceratops was a herbivore. It had a horny beak something like a turtle’s that it probably used to grab plant material, and it had some 40 teeth on each side of the jaw. These teeth were replaced every so often as the old ones wore down, sort of like crocodilians do. Back when triceratops lived, around 68 million years ago, grass hadn’t developed yet. There were prairies in parts of western North America the same way there are today, but instead of grass, the prairies were covered in ferns. Many researchers think triceratops mostly ate ferns, grazing on them the same way bison graze on grass today.
In fact, the first paleontologist to study a triceratops fossil thought it was an extinct type of bison. This was a man called Othniel Charles Marsh. To his credit, Marsh only had a little piece of a triceratops skull to examine, the piece with the brow horns. And since the brow horns of a triceratops do look a little like the horn cores of a bovid, and since this was 1887 before a lot was known about dinosaurs, and since the fossil was found in Colorado where the buffalo roam, it’s understandable that Marsh would have assumed he was looking at a gigantic fossil bison skull. He figured it out the following year after examining another skull with the nose horn intact, since bovids are not known for their nose horns, and he naturally named it Triceratops.
It’s tempting to assume that Triceratops was a herd animal, but we don’t have any evidence that it lived in groups. It was common and we have lots of fossil triceratops, especially the thick-boned skulls, but it seems to have mostly been a solitary animal.
It’s pretty obvious that the triceratops’ horns must have been for defense. It lived at the same time as Tyrannosaurus rex, which preyed on triceratops often enough that we have a lot of Triceratops fossils with T rex tooth marks in the bones. We also have some triceratops fossils with T rex tooth marks in the bones that show signs of healing, indicating that the triceratops successfully fended off the T rex and lived. But what was the frill for?
Researchers have been trying to figure this out for years. There were a lot of different ceratopsid species, many of which may have overlapped in range and lived at the same time, so some researchers suggest the frill’s size and shape may have helped individuals find mates of the same species. Triceratops has a rather plain frill compared to many ceratopsid species, which had frills decorated with points, spikes, scalloped edges, lobes, and other ornaments.
But the ornamental elements of the frills change rapidly through the generations, which suggests that they weren’t for species recognition. If that was the case, the frills would have stayed about the same to minimize confusion. Instead, they get more and more elaborate, which suggests that they were a way to attract mates who liked fancy head frills. You know, like a snazzy hairstyle.
Of course, the frill could have more than one use. It could be attractive to potential mates and also could have protected the back of the skull from T rex bites, just like a snazzy hairstyle still keeps your head warm in cold weather. Then again, in many species of ceratopsid the frill is thin and rather fragile, so it’s more likely to be just for display. It’s very likely that the frills were brightly colored or patterned.
So what were some of these other ceratopsids with strange shaped frills? I’m SO glad you asked! There were so many ceratopsids, and they all had bodies shaped roughly the same but with head frills and horns that looked very different from each other. Some had no horns, just a frill. Some just had a nose horn, some just had brow horns. The horns were shaped differently in different species, too. Researchers group ceratopsids into two major groups: the chasmosaurines, which have longer frills and usually long brow horns and short nose horns; and the centrosaurines, which typically had larger nose horns and small brow horns, and snouts that were thicker top to bottom.
Almost all the ceratopsids have been found in North America, where they were super common in the Cretaceous. But Sinoceratops was discovered in 2008 in China. It wasn’t as big as Triceratops, topping out at about 6 ½ feet tall, or 2 meters, but what it lacked in bulk it made up in head frill ornamentation. Its frill was relatively short and was edged with small horns that curve forward. Its frill also had knobs along its edge and down the middle, which is unique among all ceratopsids and may have been the base for small keratin horns. Since keratin doesn’t fossilize, we have no way of knowing. It also had two holes in the frill that made it lighter, but they would have been covered with skin (no matter what a certain movie may have led you to believe). Its single nose horn pointed almost straight up, and in front of the nose horn it had a bony knob. It basically had no brow horns, just what may have been bony knobs above its eyes.
Kosmoceratops had probably the most ornamented skull of any known ceratopsid, and maybe any known dinosaur, with 15 horns growing from it. The rear of its frill curled forward like a collar, edged with flat, pointed projections. The frill was scalloped along its sides. Its brow horns were long, pointy, and arched sideways and slightly downward. Kosmoceratops also had a cheek horn under each eye and a flattened nose horn just in front of the brow horns. It lived in what is now Utah, in the United States, some 76 million years ago, and was only described in 2010.
Pachyrhinosaurus had flattened bony nose and brow horns more properly called bosses, since they aren’t actually horns. But Pachyrhinosaurus did have horns on its frill, although the size, shape, and number of the frill horns vary from individual to individual.
These bosses resemble the base of rhinoceros horns, which as you may recall are made of keratin. Some researchers think the bosses found in Pachyrhinosaurus and other ceratopsids may have also had keratin horns growing from them.
Remember how I said Triceratops didn’t appear to be a herd animal? Triceratops is considered a chasmosaurine, and chasmosaurines all seemed to be fairly solitary animals. But the other big group of ceratopsids, centrosaurines, may have been herd animals. Pachyrhinosaurus was a centrosaurine, for instance, and several bonebeds containing dense collections of fossil pachyrhinosaurus have been found where the individuals appear to have died at the same time. The biggest found so far is in Alberta, Canada, where paleontologists have excavated thousands of bones, from full grown adults to babies. Researchers suggest a herd of the animals may have died trying to cross a flooded river. The species of Pachyrhinosaurus found in the Alberta bonebed had both bosses and short brow horns.
Even though only one species of ceratopsid has been discovered in Asia so far, earlier basal forms were common in Asia. Protoceratops, which only stood about two feet tall, or 60 cm, lived in what is now the Gobi Desert in Mongolia around 80 million years ago. Researchers think some of these early species in the genus Protoceratops migrated into North America on the Bering land bridge, where they evolved into ceratopsids.
Protoceratops looked like a mini ceratopsid with a simple neck frill and no horns. We have a lot of Protoceratops fossils and some of them are frankly amazing.
For instance, a Protoceratops fossil found in 1965 was preserved with its own footprint in the ground near it. The fossils of baby protoceratopses have been found together in one nest, which suggests the parents cared for their young. We even have a fossil of a protoceratops and a Velociraptor that both died together while fighting. The velociraptor’s hind leg is extended where it kicked protoceratops with its vicious claws, but the velociraptor’s arm is in protoceratops’s jaws, broken.
Fighting dinosaurs. It’s one of those things that makes life worth living, you know?
You can find Strange Animals Podcast online at strangeanimalspodcast.com. We’re on Twitter at strangebeasties and have a facebook page at facebook.com/strangeanimalspodcast. If you have questions, comments, or suggestions for future episodes, email us at strangeanimalspodcast@gmail.com. We also have a Patreon if you’d like to support us that way.
Thanks for listening!