Podcast: Play in new window | Download (Duration: 13:22 — 15.4MB)
Pre-order your tiny pin friend via our Indiegogo campaign!
This week we talk about some springtime animals! Sort of! Thanks to Derek and Nikita for their suggestions!
Happy birthday to Lillian, Hannah, and Derek! What a busy birthday week! Everybody gets cake!
Further reading:
There’s more than one way to grow a beak
A male river chub. “It’s not funny guys, put me down guys” (photo by Bill Hubick):

Busy busy busy building a big big nest (photo from site linked to above):

Got a rock (photo from site linked to above):

One bilby:

Two bilbies:

Easter bilbies not bunnies:

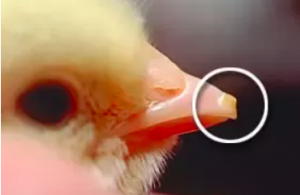
Egg tooth:
The red jungle fowl is the wild ancestor of the domestic chicken:

Modern domestic chickens:

Show transcript:
Welcome to Strange Animals Podcast. I’m your host, Kate Shaw.
It’s springtime in the northern hemisphere, with spring festivals like Easter coming up fast. This week let’s look at three animals that represent springtime, sort of. Thanks to Derek and Nikita for suggesting two of the animals we’ll learn about this week!
Before we start, though, two things! One, I’m running a little crowdfunding campaign to have some enamel pins made. I won’t spam you about it like our big Kickstarter for the book last fall, but there will be a link in the show notes if you want to take a look. There are three designs, a narwhal, a capybara with a tangerine on its head, and a not-terribly-accurate thylacine. The campaign is called Tiny Pin Friends and it’s on Indiegogo.
https://www.indiegogo.com/projects/tiny-pin-friends/x/2964999#/
Two, it’s birthday shout-out time! This week we have not one, not two, but THREE birthday shout-outs! You know what that means, of course. It means we all need to be celebrating all week! A great big happy birthday to Lillian, Hannah, and Derek! And yes, birthday Derek is the same Derek who suggested one of the animals this week!
In fact, let’s start with his suggestion, a fish called the river chub. It’s a little fish that only grows a little over a foot long at most, or 33 cm, although it’s usually much smaller than that. It’s common in fast-moving streams and rivers throughout North America, especially in the Appalachian Mountains and surrounding areas.
The river chub isn’t all that exciting to look at, unless of course you’re a fish enthusiast or a river chub yourself. It’s greenish-silver above and pale underneath with orange fins. Males are larger than females and during breeding season, in late spring, the male turns purplish-red, his head enlarges, and he develops tubercles on the front part of his head that look sort of like white rhinestones.
His physical changes aren’t just to attract a mate. The male river chub builds a pebble nest by picking up little stones and moving them to just the right spots, so by having a more robust head and broad mouth, he can pick up bigger stones. And he picks up a LOT of stones, as many as 10,000 of them, which he arranges and rearranges.
Females are attracted to well-made nests. After a female lays her eggs in the nest, the male fertilizes the eggs and then spends the next week or so defending them by head-butting other males and potential predators, until the eggs hatch into larvae.
The pebble nests help other animals too. Over 30 species of fish use the nests as spawning sites once the river chub’s eggs hatch. Good job, river chub, helping out all those other fish!
Next, a while back Nikita suggested we learn about the bilby. It’s not springtime right now in Australia where the bilby lives, but the Christian holiday of Easter is still celebrated at the same time as it is in the northern hemisphere. Instead of chocolate Easter bunnies, in Australia they also have chocolate Easter bilbies.
In 1968, a nine-year-old girl named Rose-Marie Dusting wrote a story called “Billy the Aussie Easter Bilby.” When she grew up, Rose-Marie published the story as a picture book, which became popular enough that it inspired people in Australia to start talking about the Easter bilby instead of the Easter bunny. Starting in 1991 there was a big push to change from Easter bunnies to bilbies. Rabbits are an invasive species in Australia and do a lot of damage, and in fact they’ve almost driven the bilby to extinction. The lesser bilby did go extinct in the 1950s but the greater bilby is hanging on despite introduced predators like cats and foxes, rabbits and other introduced animals that eat all their food, and habitat loss.
The bilby has silky fur that’s mostly gray in color, and it has long pink ears that look sort of like a rabbit’s. It’s sometimes called the rabbit-eared bandicoot because of its ears. It has a long, pointy muzzle that’s pink and a long tail that’s black with a white tip, and it’s about the size of a cat but with shorter, thinner legs. It has a good sense of smell and good hearing, naturally, but its big ears are also useful for shedding heat. This is important since it often lives in hot, dry areas.
The bilby is nocturnal and spends the day in one of several burrows it digs in its territory. Not only are the burrows up to almost 10 feet long, or 3 meters, but they can be up to 6 feet deep, or 2 meters, with multiple exits. Digging such large, deep burrows not only keeps the bilby cool on hot days, it helps improve soil quality and provides shelter for lots of other animals that move in when the bilby isn’t home.
The bilby eats a lot of plant material, including seeds, fruit, bulbs, and tubers, along with eggs and various types of fungus, but it also eats insects, spiders, grubs, snails, and other small animals. It gets all of the moisture it needs from its diet. Its tongue is long and sticky, which helps it gather termites and other insects more easily, and its ears are so sensitive that it can hear insects moving around underground. It will actually put its ear to the ground to listen, then dig the insect up.
A mother bilby usually has one or two babies at a time that stay in her pouch for a little under three months. Her pouch is rear-facing so that sand and dirt don’t get onto her joeys when she digs a new burrow. Once her joey leaves the pouch, she hides it in one of her burrows and comes to feed and take care of it for another few weeks, until it’s ready to strike out on its own. In a lot of marsupials, the joey will come and go from the pouch as it grows older, but by the time the bilby’s joey is ready to emerge from the pouch, she already has a new baby or two ready to be born, so she needs her pouch for the new joeys.
Sales of some brands of chocolate Easter bilbies raise money to help bilby conservation efforts. And here I thought there was no way to improve on chocolate.
We’ll finish with the humble domestic chicken. Chickens are symbols of springtime because that’s when they start laying a whole lot of eggs. Most birds only lay eggs after mating, but chickens have been selectively bred so that the females, called hens, start to lay unfertilized eggs once they’re adults. The eggs you buy at the grocery store are unfertilized. Some people think those little whitish strings on either side of the yolk are embryonic baby chicks, but that’s not the case. Those strings are called chalazae [ka-LAYzee] and they help keep the yolk from moving around too much inside the egg.
Modern domestic chickens are descendants of wild birds called jungle fowl that evolved in parts of Southeast Asia some 50 million years ago. Humans domesticated the red jungle fowl at least 8,000 years ago, probably independently in different areas, and they’ve spread around the world as people migrated from place to place. The red jungle fowl is still around in the wild, too. It looks like a chicken.
Like all birds, jungle fowl descended ultimately from theropod dinosaurs. This included Tyrannosaurus rex, which means you’ll occasionally hear people say that chickens are direct descendants of T. rex. While chickens and other birds are related to T. rex, you wouldn’t find a T. rex in a chicken’s direct ancestry even if you could follow it back 66 million years, although you would find much smaller theropods. You’d have to go back farther than 66 million years, though, because paleontologists think theropods started evolving bird-like features some 160 million years ago.
You may have heard the saying, “That’s as scarce as hen’s teeth” to indicate something that’s not just rare, it’s basically non-existent. That’s because chickens, like all modern birds, don’t have teeth. Most birds and reptiles do grow what’s called an egg tooth, which actually looks like a little spike at the tip of the bill, or the nose in reptiles. It helps the baby break out of its egg, after which it either falls off or is reabsorbed. But it’s not a real tooth.
In late 2020 paleontologists announced they’d found a fossil skull on the island of Madagascar, dated to 85 million years ago, that shows an animal with a beak. The animal resembles a small theropod dinosaur in some ways and resembles an early bird in other ways, but it has features never before seen in either. Its snout is elongated but deep with a heavy bill that looks a little like a toucan’s bill. The bill doesn’t have teeth along the jaws, although other early birds found from around the same time do. That means that not only did birds stop needing teeth as early as 85 million years ago, toothlessness must have evolved repeatedly in various species. However, the new animal’s beak does have teeth at the very tip of its mouth.
Recent research suggests that birds and their ancestors evolved toothless beaks instead of toothy snouts because they had such specialized diets. There were probably also other benefits to having beaks instead of teeth. Some research suggests it might have helped speed up egg hatching. Other studies suggest the lack of teeth lightened the bird’s head and improved flight.
Occasionally a chicken embryo bears a recessive trait called talpid. It’s a lethal mutation, but talpid chick embryos do sometimes live in the egg for a couple of weeks before dying. Genetic researchers study talpid chickens for various reasons, and at one point a researcher named Matthew Harris noticed something odd on the beak of a talpid chicken embryo. It had tiny bumps along the edge that looked like teeth.
Harris took his findings to biologist John Fallon, who verified that the structures are actually teeth, not just serrations. They develop from the same tissues that form teeth in mammals, but the teeth don’t resemble mammal teeth. Instead they’re conical and pointy like a dinosaur’s teeth.
Harris eventually engineered a virus that mimicked the mutation’s molecular signals. Introducing the virus into chickens without the talpid mutations resulted in the chickens developing teeth, although they were reabsorbed into the beak after developing.
So I guess hen’s teeth are still as scarce as hen’s teeth. Also, I don’t really know how we made it here from springtime animals, but here we are.
You can find Strange Animals Podcast at strangeanimalspodcast.blubrry.net. That’s blueberry without any E’s. If you have questions, comments, or suggestions for future episodes, email us at strangeanimalspodcast@gmail.com. If you like the podcast and want to help us out, leave us a rating and review on Apple Podcasts or Podchaser, or just tell a friend. We also have a Patreon at patreon.com/strangeanimalspodcast if you’d like to support us for as little as one dollar a month and get monthly bonus episodes.
Thanks for listening!