Podcast: Play in new window | Download (Duration: 11:49 — 11.8MB)
We’re not looking at just any old insectivores in this episode, we’re looking at the big three of ant-eating mammals: the giant anteater, the aardvark, and the pangolin!
A giant anteater and baby:

Teeny anteater mouth alert! Also long tongue:

An aardvark walking with style:

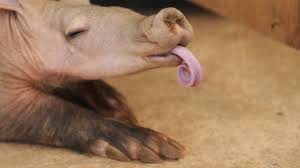
An aardvark. Look at that tongue! And those claws!
An Indian pangolin. Please do not eat:

A pangolin ball. Please do not kick:

Save the Pangolins organization
Show transcript:
Welcome to Strange Animals Podcast. I’m your host, Kate Shaw.
This week we’re going to learn about the anteater, the aardvark, and the pangolin, all of them specialized eaters of ants. Are they related? How do we tell them apart?
The anteater is a South and Central American animal related to sloths and, more distantly, armadillos. The aardvark is an African animal related to several rodent-like animals including the golden mole, which is not a mole, and the elephant shrew, which is neither an elephant nor a shrew. Although, as it happens, the elephant shrew is actually related to the elephant. So is the aardvark, although these connections are pretty darn distant. The pangolin is an Asian and African animal that’s not very closely related to anything.
Let’s start with the giant anteater.
The giant anteater can grow over seven feet long if you include the tail, or more than 2 meters. It’s brown and gray with markings that look like go-faster stripes. Its head is small and elongated. You know how a cartoon character can cram its head into a bottle and its head stays bottle-shaped? It kind of looks like the giant anteater did that. Its snout is shaped like a tube, with nostrils and a tiny mouth at the end. It can’t open its jaws very far. It has a short upright mane along its spine all the way down its back, which blends with its bushy tail. Its tail is so awesomely furry that when an anteater sleeps, it covers its body with its tail like a blanket.
Anteaters eat ants, although they also love termites and will eat other small insects and insect larvae. The giant anteater uses its massive front claws to dig into anthills. Then it flicks its tongue really fast, catching insects with a combination of tiny hooklets on the tongue and sticky saliva. An anteater’s tongue is over two feet long, or 60 cm, so long that when the anteater isn’t actually eating, the tongue rolls up at the back of its skull. The base of its tongue is attached not to its throat but to its sternum, also called the breastbone.
A feeding anteater eats as many insects as it can catch in a minute or two, then moves on to find a new anthill. It does this to avoid as many stings and bites as possible. To conserve energy, the anteater’s body temperature is low to start with and drops when the animal is asleep.
The anteater doesn’t have teeth. It crushes insects against the top of its mouth before swallowing them, and its stomach acts like a bird’s crop. The anteater may deliberately eat sand or grit the way birds do to help pulverize the insects it’s eaten. Its eyesight isn’t very good so it hunts mostly by scent.
The giant anteater knuckle-walks on its forepaws because its front claws are so big. When it feels threatened, it will rear up on its hind legs and spread its forelegs so it can slash with its claws. Anteaters can kill jaguars and other predators, including humans. Occasionally anteaters will fight over territory, especially males. Sometimes during a fight, one anteater will climb on the other one and ride it around, which probably really annoys the anteater that’s being ridden.
The female anteater has one baby at a time, which rides on its mother’s back until it’s big enough to keep up with her on its own. Its markings blend with its mother’s so predators don’t notice it.
So that’s the giant anteater. Now let’s look at the aardvark.
The aardvark is about the same size as the anteater and also eats ants, termites, and other insects. It has a long head, but unlike the anteater, it does have teeth. The incisors and canines it’s born with fall out when it’s an adult, and it never regrows them, but it does retain its cheek teeth. The teeth are small and grow constantly throughout the aardvark’s life, since they wear down quickly due to the lack of enamel.
The aardvark isn’t super furry like the anteater. Its body is shaped something like a pig with a long tail, and it has sparse hair and long ears, whereas the giant anteater has small ears. It’s mostly nocturnal and sleeps during the day in its burrow, where it’s cooler. While it doesn’t have huge claws on its forefeet, it does have tough hoof-like nails that it uses to break apart termite nests and dig burrows. Its skin is thick and it can run and dig quickly to escape predators. It can also swim well.
The aardvark has a good sense of smell and hearing, but its eyesight isn’t all that great. Its snout is more piglike than the anteater’s, with large nostrils protected by hair. Its tongue isn’t as long as the anteater’s, only about a foot long, or 30 cm.
In addition to ants and termites, the aardvark eats one other thing, a fruit called the aardvark cucumber. It’s an actual cucumber, a round fruit about the size of a small child’s fist, but the fruit grows underground. It has a water-resistant skin that keeps it from rotting while it waits for months for an aardvark to dig it up and eat it. The aardvark is the only animal that spreads the aardvark cucumber’s seeds. Researchers think the reason aardvarks have teeth at all is to eat these cucumbers, and that it eats the cucumbers because of their high water content. The seeds travel through the aardvark’s digestive system, and since the aardvark buries its poop like a cat, the cucumber seeds are all ready to sprout.
Female aardvarks have one baby at a time, which stays in the burrow until it’s old enough to follow its mother around. The aardvark ranges widely while it searches for insects, and if it encounters a predator it may dig a burrow to hide in. It can dig a burrow the length of its body in only about five minutes. Sometimes it will dig a temporary burrow to rest in. Empty aardvark burrows make great homes for other animals, from warthogs to various bird species. Even a type of bat roosts in old aardvark burrows.
So that’s the aardvark. Now let’s learn about the pangolin.
At first glance, the pangolin looks nothing like its ant-eating friends from other lands. It’s a mammal, but it’s covered in scales except for its belly and face. Sometimes it’s called the scaly anteater, in fact. Its sharp-edged, overlapping scales are made of keratin. When it’s threatened, it rolls up in a ball with its tail over its face.
The pangolin’s body shape is very similar to the giant anteater’s and the aardvark’s. There are a number of species in three genera of the family Manidae, but we’ll look at just one today, the Indian pangolin. It lives in India and surrounding areas and is about four feet long, or 120 cm, including the tail. It has a humped back like an aardvark, small ears like a giant anteater, and like both those animals its legs are relatively short. Its muzzle is long with a nose pad at the end, it has a long sticky tongue, and it has no teeth. It’s nocturnal and lives in burrows, and it uses its big front claws to dig into termite mounds and ant colonies. Like the others, it has poor vision but a good sense of smell.
It’s mostly solitary and gives birth to one baby at a time, or rarely twins. The baby rides on its mother’s tail, and if she has to roll up to protect herself, she holds her baby against her belly and rolls up around it. Newborn pangolins have soft scales.
There used to be an enormous species of pangolin in Asia, whose remains have been found in Java, India, and other places. The bones date to around 45,000 years ago but we don’t have enough remains to get a good idea of when the giant Asian pangolin actually went extinct. It was probably around eight feet long including the tail, or almost 2.5 meters. People native to an island called Rintja in Indonesia tell stories about the veo, a scaly animal ten feet long, or three meters, that sounds exactly like a giant pangolin. So it’s possible that these giant pangolins didn’t die out until humans encountered them.
Unfortunately for the pangolin, its scales make it sought after by humans for decoration. People also eat them. In some countries, like Vietnam and China, pangolin meat is an extremely expensive delicacy, which means poachers can get a lot of money for them. Habitat loss is also making it tough for the pangolin. All species of pangolin in Asia are endangered or critically endangered, while all species of pangolins in Africa are vulnerable. Pangolins also don’t do well in captivity so it’s hard for zoos to help them.
Pangolins just walk to trundle around eating ants. Why are people so mean?
I’ll put a link in the show notes to the Save Pangolins organization if you want to contribute. All sales of cute pangolin merch from their store also goes toward helping stop pangolin poaching and smuggling.
Scientists used to think that anteaters, aardvarks, and pangolins were closely related since they share so many similarities. Instead, they show convergent evolution, where they inhabit a similar ecological niche and therefore evolve to look similar. You know what the pangolin is most closely related to? Carnivores, including cats and dogs and bears.
So it’s probably safe to assume at this point that if you want to eat mostly ants and termites, you need a long thin snout, a super-long sticky tongue, and big claws for digging. Personally, I would rather have pizza.
You can find Strange Animals Podcast online at strangeanimalspodcast.com. We’re on Twitter at strangebeasties and have a facebook page at facebook.com/strangeanimalspodcast. If you have questions, comments, or suggestions for future episodes, email us at strangeanimalspodcast@gmail.com. If you like the podcast and want to help us out, leave us a rating and review on Apple Podcasts or whatever platform you listen on. We also have a Patreon if you’d like to support us that way.
Thanks for listening!