Podcast: Play in new window | Download (Duration: 9:26 — 10.5MB)
Welcome to 2024! Let’s learn about some exciting new discoveries in our own family tree!
Further reading:
476,000-Year-Old Wooden Structure Unearthed in Zambia
Mysterious 300,000-year-old skull could be new species of human, researchers say
Show transcript:
Welcome to Strange Animals Podcast. I’m your host, Kate Shaw.
It’s time to start the new year off with an episode that has me really excited. I was initially going to include this in the updates episode that usually comes out around summertime, but I just can’t wait. In 2023, scientists discovered what they think might be a new lineage of extinct human ancestors!
We’ll come back to that in a moment, but first I want to highlight another amazing human-relateded discovery from 2023.
And just to let you know, I am going to be using the words “humans” and “people” and “hominins” more or less interchangeably. I try to make it clear when I’m talking about Homo sapiens versus other species of ancient hominin, but these are all our ancestors–in many cases our direct ancestors–so they’re all people as far as I’m concerned.
As you may know, especially if you’ve listened to previous episodes where we’ve discussed ancient human ancestors, the ancestors of all humans evolved in Africa. Specifically, we arose in the southern part of Africa, in areas that had once been dense forest but gradually changed to open woodland and savanna. Because there weren’t very many trees, our far-distant hominin ancestors, the australopiths, no longer needed to be able to climb trees as well as their ape cousins. Instead, they evolved an upright stance and long legs to see over tall grasses, and the stamina to run after the animals they hunted until the animal was exhausted and couldn’t run anymore. Once our ancestors were walking on two legs all the time, their hands were free to carry babies and food and anything else they wanted.
Being fully bipedal meant that women had a harder time giving birth, since the pelvis had to change position to allow them to walk and run, so babies started being born when they were smaller. This meant the babies needed a whole lot more care for a lot longer, which meant that family groups became even more important and complicated. One thing we’ve learned about sociability in animals is that it leads to increased intelligence, and that’s definitely what happened with our long-distant ancestors. As their brains got bigger, they became more creative. They made lots of different types of tools, especially weapons and items that helped them process food, but eventually they also made artwork, baskets, clothing, jewelry, and everything else they needed.
All this took a long time, naturally. We know Australopithecus used stone tools over three million years ago, but we don’t have evidence of human ancestors using fire until a little over 1.5 million years ago. Homo sapiens was once thought to have only evolved around 100,000 years ago, maybe less, but as scientists find more remains and are able to use more sophisticated techniques to study those remains, the date keeps getting pushed back. Currently we’re pretty certain that actual humans, if not the fully modern humans alive today, arose about 300,000 years ago and maybe even earlier. Homo sapiens evolved from Homo erectus, which arose about two million years ago and went extinct about 100,000 years ago. They were probably the first hominin to use fire, which allowed humans to start migrating longer distances into colder climates. They might also have communicated with language. Basically, Homo erectus was a lot like us but not quite us yet.
The modern-day country of Zambia is in the middle of south-central Africa, and naturally it’s been home to humans and our ancestors for as long as humans have existed. One especially important part of Zambia is also one of its most beautiful places, Kalambo Falls, which is really close to the equally important and beautiful country of Tanzania. Scientists have known that humans of one kind or another have lived around Kalambo Falls for at least 447,000 years, long before Homo sapiens actually evolved.
When a team of archaeologists excavated a sandbar near the falls in 2019, they were surprised to find wooden artifacts. Wood doesn’t usually preserve for very long and the site they were excavating was quite old. In addition to wooden tools, they found two logs that had been shaped and notched to allow them to fit together securely. The researchers thought the logs had once been part of a structure like a walkway that would keep people’s feet out of the mud and water, or possibly the floor of a wooden structure used to store food. It might even have been the floor of a little house.
Wood can be dated with simple tests to find out its age, but the test is only useful for trees that died within the last 50,000 years. Anything older than that is just, you know, older than 50,000 years. The tools and logs tested as older, which the scientists expected. Fortunately there are other ways to date older wood, but the results of those tests were surprising even to the scientists. The tools were at least 324,000 years old, possibly as much as 390,000 years old, but the logs were even older, about 476,000 years old.
Remember, Homo sapiens didn’t even evolve until about 300,000 years ago. That means humans didn’t make those tools or build anything with those shaped logs. Some other hominin did, although we’re not sure who. Even more exciting, close examination of the logs suggests that they may have been subjected to fire at some point. That might mean a natural fire or it might mean that the people who were building with the logs were also using fire as much as two million years before we thought people were using fire.
Obviously scientists are going to look carefully for more clues about who might have shaped these logs and when. Hopefully we’ll learn more soon.
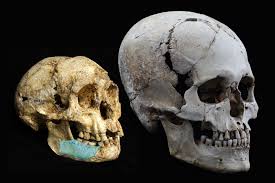
Around the same time that scientists uncovered the wooden items in southern Africa, another discovery was made in 2019, this one in East China. A team found a jaw, skull, and leg bones of a hominin that didn’t match up to any known human ancestor. The bones were dated to 300,000 years ago, at the dawn of Homo sapiens. Other hominins had migrated to eastern Asia long before this, however, including populations of Homo erectus.
The newly discovered bones don’t belong to Homo erectus, though. They don’t belong to Homo sapiens either, or any other known hominin. They represent a completely new hominin, and at the moment scientists don’t know where exactly they fit in our own family tree.
The bones show traits found in modern humans, like a flat face, but lack other uniquely human traits, most notably a chin. Homo sapiens have chins, unlike every other hominin, and no one’s sure why. It might have something to do with speech or maybe early humans with chins were just considered more attractive, and now everyone has a chin.
The mystery hominin is still being studied, but preliminary findings indicate that we might have discovered the ancestor of a very close relation. The bones show some traits also found in Neandertals, our very closest evolutionary cousins, even though they’re extinct. There’s a possibility that this new hominin gave rise to another line of very close human relations, one we don’t have any fossils of yet.
I know there are a lot of excited scientists wanting to learn more about the hominin bones. Hopefully more bones will turn up soon so we can get a better idea of who this distant relative is. It’s a little too early to throw them a welcome home party, but maybe we can start planning it now.
You can find Strange Animals Podcast at strangeanimalspodcast.blubrry.net. That’s blueberry without any E’s. If you have questions, comments, or suggestions for future episodes, email us at strangeanimalspodcast@gmail.com. We also have a Patreon at patreon.com/strangeanimalspodcast if you’d like to support us for as little as one dollar a month and get monthly bonus episodes.
Thanks for listening!