Podcast: Play in new window | Download (Duration: 18:05 — 18.3MB)
It’s almost Halloween!! We’ve got a great episode this week about rats–ordinary rats, giant rats, and the strange phenomenon called the rat king.
- Buy my book, Skytown!
- Buy me a coffee!
- Donate to our Patreon and get bonus episodes!
Speaking of bonus episodes, I’ve unlocked a few for anyone to listen to. Just click through and listen in your browser, no login required:
Irrawaddy dolphins and Dracula ants
Further viewing:
A squirrel king video (the squirrels were captured and freed by a veterinarian later)
A typical brown rat, a la Ratatouille:


A typical black rat:

A typical fancy (aka domesticated) rat:

A giant pouched rat heading to work to sniff out landmines:

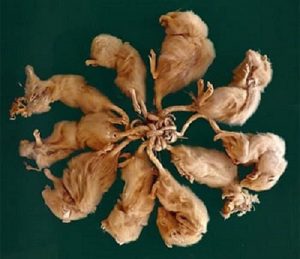
Two rat kings (preserved):

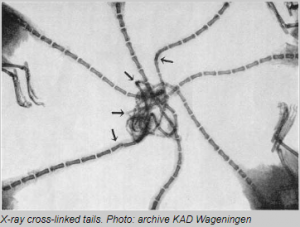
An X-ray of a rat king’s tails (the arrows show places where the tails are fractured):
Show transcript:
Welcome to Strange Animals Podcast. I’m your host, Kate Shaw.
It’s finally the Halloween episode! I hope you all have your costumes ready to go! This week we’re going to learn about an animal sometimes associated with Halloween, the rat, including some mystery rats.
But first, my yearly housekeeping and promo-ing! You can still pick up a copy of my fantasy adventure book Skytown, available from Fox Spirit Books. I’ll put a link in the show notes. It has some adult language but is otherwise suitable for younger teens through adults. I’m also working on a nonfiction book associated with Strange Animals Podcast, but we’ll see how that goes.
If you want to support the show financially, I am always happy to take your money. We’ve got a Ko-fi account where you can tip me the cost of a coffee, or more, and we’ve also got a Patreon account if you want to set up recurring donations and get bonus episodes in exchange, as well as other perks. There are links to both in the show notes and on the website, strangeanimalspodcast.blubrry.net. Also on the website we’ve got two pages now that list what animals we’ve covered so far. One page is for everything, the other is just for cryptids for those of you who are just here for the mystery animals.
Speaking of Patreon bonus episodes, I’ve unlocked a few episodes so that anyone can listen to them. They won’t show up in your feed, but there are links in the show notes and you can just click on the link and listen in your browser. You don’t need a Patreon login or anything. This time I’ve unlocked some fun ones, including an episode about animal ghosts from last Halloween.
Now, on to the rats.
The presence of rats is usually considered bad luck, undoubtedly because rats evolved to take advantage of humans’ habit of storing grain for later. If rats ate the grain, humans and their livestock could starve. But rats are also considered bad omens or evil when they’re just going about their lives, being rats.
The rat is a rodent that resembles a big mouse, not surprising since they’re closely related. There are lots of rat species and subspecies, but the most well known are the black rat and brown rat. These are the ones most likely to live in cities and houses, especially the brown rat. The brown rat is also sometimes called the Norway rat even though it’s originally from Asia.
The brown rat is a relatively large rodent, up to about a foot long, or 30 cm, with a tail that’s nearly as long. The black rat is a little smaller and less bulky, with larger eyes and ears, and has a tail that’s longer than its body. Male rats are usually larger and heavier than females. A rat’s tail is bare of fur and has thin skin, and if a predator grabs it by the tail it can shed the skin of the tail, called degloving. The skin will grow back, but until it does the tail is prone to infection. That’s one of the reasons why you should never pick up a pet rat by the tail. Also, picking a rat up by the tail can injure it.
The domesticated rat, also called the fancy rat, is descended from the brown rat. Rat catchers, especially a man named Jack Black, whose title was Royal Rat Catcher and who lived in the mid-19th century, kept interestingly patterned or colored rats he caught in his job. At the turn of the 20th century, fancy mice were a popular pet in Europe, and in 1901 a woman named Mary Douglas suggested the UK group called the National Mouse Club also accept rats. I don’t know about you, but I would totally join the National Mouse Club just for the name. It’s actually still around today, in fact, and I just looked and it costs money to join, so never mind. It’s not like I have any pet mice anyway. Domesticated rats are intelligent, clean pets, and friendly if they’re properly socialized. Rats do leave scent trails for other rats by releasing small amounts of urine as they move around, though, so be aware of this before you let your pet rat run around the house.
The rat has good hearing, smell, and sense of touch, with lots of sensitive whiskers to help it find its way even in the dark. Many of the sounds it makes are in the ultrasonic range so aren’t audible to human ears, including laughter. That’s right, rats laugh. It’s more of an ultrasonic chirping sound, but it occurs when rats are playing, and when a pet rat is tickled by its owner. Young rats laugh more than old rats.
This is what a rat laugh sounds like, slowed down so it’s audible to human ears.
[rat laughing/chirping]
The rat can also swim well, dig well, and shows signs of being surprisingly intelligent. It’s an omnivore that will eat anything it can find or catch. It will kill and eat small animals or sometimes even larger animals like ducks. Some rat populations have learned to dive for mollusks and catch fish.
Rats are social animals and live in large groups, usually in burrows with extensive tunnel systems. In cities, instead of digging burrows rats will live in sewers, alleys, and buildings. Rats go where people go, and they live where people live. While the rat is mostly nocturnal, it’s not unusual to see a rat during the day too.
Rats do carry diseases which they can spread to humans and other animals through their urine and feces, through bites, or through fleas or mites. You’ve probably heard that rats carry a type of flea that spreads the black death, which killed millions of people throughout the 14th century and later. Researchers think that the black death was an especially dangerous version of the bubonic plague. The bubonic plague is actually still around, but these days it’s rare, usually not as dangerous as the version of the disease spread in the middle ages, and can be cured with modern medicine. Humans aren’t the only animals that can catch the plague, by the way. So can cats, dogs, and the rats themselves.
So a rat can grow to about a foot long not counting the tail, or 30 cm. Even a big rat doesn’t weigh more than about two pounds, or a little under a kilogram. But what about giant rats? Or, you might say, rodents of unusual size.
Occasionally someone reports seeing or killing a rat twice the normal size or more, but while you can find pictures of giant dead rats online, it’s really easy to fake that kind of picture. Some are obviously examples of forced perspective, where the rat looks big because it’s actually quite close to the camera, some are plain old photoshopped, and some aren’t actually rats at all.
There are some rodents that look a lot like regular old rats but are much larger. Most are rare or not well known outside of its native habitat, like the Sumatran giant rat that grows up to two feet long, or about 61 cm, not counting its tail. It’s brown with longer fur than the actual brown rat, and it lives in parts of southeastern Asia, but it’s only distantly related to the rat.
The African giant pouched rat is also only distantly related to the actual rat although it looks quite similar. Unlike rats, but like some other rodents, it has cheek pouches that it uses to carry food. It’s bigger than the brown rat, up to about a foot and a half long not counting the tail. or 45 cm, and until 2003 it was a popular exotic pet in the United States. But in 2003, some giant pouched rats imported to the midwest from Africa spread a disease called monkey pox to other animals that were then all sold as pets, especially prairie dogs. In the next five weeks 71 people were infected with the disease. Fortunately no one died, but monkey pox is related to smallpox and can be deadly to humans. As a result of the outbreak, the United States no longer allows any rodent to be imported from Africa.
Also in 2003, the remake of a horror movie about a man named Willard and his rats was released. The rat named Ben was played by a giant pouched rat. I have not seen the movie because I’m a wimp about horror movies, but if you like them and are, you know, a grown-up type person, apparently that was a pretty good one. The original movie was released in 1971 with a sequel in 1972, and all I know about it is that Michael Jackson sang the theme song, which is probably the only song I know that’s about a rat. It’s a pretty song.
The giant pouched rat is sometimes trained to detect landmines, since it has a good sense of smell and isn’t heavy enough to set off the landmines. The problem is that the giant pouched rat doesn’t actually breed well in captivity, so breeding pouched rats that are especially tame and good at detecting explosives is proving to be difficult. Researchers aren’t even sure what causes the females to come into season so that they can have babies. In other rodents, the release of certain hormones controls this cycle, but that doesn’t seem to be the case in giant pouched rats.
As if the bomb-sniffing and acting skills weren’t enough, the giant pouched rat has also been trained to detect tuberculosis in children. The rat does this by sniffing samples of spit taken from children, and a trained rat is so good at detecting the infection that it’s actually 68% more accurate than the standard medical test.
Not to be outdone, researchers in North America are working on ways to train brown rats as search and rescue animals for areas where search and rescue dogs can’t enter.
We got a little off-topic there but you have to admit, the giant pouched rat is a pretty neat rodent, even if it’s not actually part of the rat family.
Another rodent once thought to be a type of rat was a mystery for centuries. In 1503 the Florentine explorer Amerigo Vespucci reached Brazil, and while he was there he visited the volcanic island Fernando de Noronha and wrote about it later. One of the things he mentioned was that the island was home to very large rats.
Since Vespucci was the first European ever to visit the island, and no one from anywhere in the world was living on it at the time, the rats he saw can’t have been the rats he was used to. That would have been the black rat, since the brown rat hadn’t spread throughout Europe yet. It did so later, outcompeting the black rat in most environments. But in 1503, the black rat was the one Vespucci would have known, and the rats he saw on the island were bigger.
Other explorers and sailors visited the island in the years after 1503, and by 1888 when biologists came looking for the very big rat, all they found were the descendants of black rats brought there by ships.
Then, in 1973 paleontologists from Brazil and the United States visited the island to see what had once lived there. And they found remains of the very large rat. It turns out that the rat wasn’t actually a rat, although it was a rodent. And while it was larger and heavier than the black rat, it wasn’t enormous. It was about the size of a typical brown rat, in fact. Ironically, it was probably driven to extinction by the ship rats that colonized the island soon after Vespucci visited.
Vespucci’s rat has been named Noronhomys vespuccii and was given its own genus. Reseachers think that its ancestor might have been semiaquatic like some rodents that still live in South America and that are related to Vespucci’s rat. Rodents that were already in the water would have been occasionally swept out to sea and floated or swam to the island. But once a population of the rodents was established on the island, they evolved to be exclusively terrestrial.
But let’s get back to actual rats. A lot of people are afraid of rats, and it’s true that a cornered rat will bite to defend itself. Rats still carry diseases too. As a result, there are lots of superstitions about rats. For instance, according to folklore than goes back almost two thousand years, the best way to get rid of rats is to write the rats a polite letter requesting that they leave. Fold it up carefully and slide it into the rat’s hole. I am pretty sure that one doesn’t work.
Rats are supposed to be able to foretell misfortune and death. If a rat chews up someone’s clothes or belongings, that person is supposedly going to die soon. If you see rats leaving a ship, it’s an omen that the ship is going to sink. I’ve been reading about superstitions, and it’s amazing how many animals are supposed to foretell death and bad luck. It’s almost like people are trying to blame an animal for random events.
Finally, it wouldn’t be Halloween without something spooky, weird, or gross, or better yet, all three. So let’s learn about something called the rat king.
A rat king isn’t one animal but a group of rats joined together by their tails. This sounds like something out of folklore but it’s actually a real occurrence, although it’s rare. The oldest report known dates to 1564, but specimens are occasionally uncovered even today. All reliable reports of rat kings are of black rats. The black rat has a long, thin, flexible tail that it uses to help it climb.
Not much is known about how rat kings form, but the most widely accepted suggestion is that a group of rats huddling together for warmth get their tails tangled together without realizing it. When each rat tries to separate itself from the group by pulling, the knot tightens. Eventually the rats are permanently stuck together.
It seems reasonable to think that a bunch of rats stuck together by their tails wouldn’t survive long. They’d starve to death or kill each other trying to get free. But a rat king made up of seven rats found in the Netherlands in 1963 was examined and even X-rayed to learn more about it, and where the tails were intertwined there was some evidence of calluses forming. This suggests the rats may have survived for some time.
Most rat kings are made up of young rats, possibly siblings sharing a nest. It’s possible the mother of the 1963 rat king fed them and kept them alive until they were discovered by a farmer, who killed them.
Rats aren’t the only animals found with their tails knotted together. It happens to squirrels occasionally too. If you check the show notes, I’ve included a link to a video of a squirrel king. In the case of squirrels, pine sap and nesting material can glue or tangle the tails of young squirrels together, and we have not just video evidence from 2013 and 2018, but the evidence of veterinarians who managed to separate the squirrels in both cases so they wouldn’t die.
So the rat king sounds horrifying and kind of is, but it’s also sad and not really spooky at all. It’s funny how often understanding something that sounds scary makes you realize it’s not actually all that scary after all. People and rats may not always get along, since rats are very interested in eating food people want to keep for ourselves. But rats laugh, so they can’t be all bad.
You can find Strange Animals Podcast online at strangeanimalspodcast.blubrry.net. That’s blueberry without any E’s. If you have questions, comments, or suggestions for future episodes, email us at strangeanimalspodcast@gmail.com. We also have a Patreon if you’d like to support us that way.
Thanks for listening, and happy Halloween!