Podcast: Play in new window | Download (Duration: 25:36 — 24.8MB)
Subscribe: | More
Let’s learn about the LUNGFISH, which deserves capital letters because they’re fascinating and this episode took so flipping long to research! Mysteries abound!
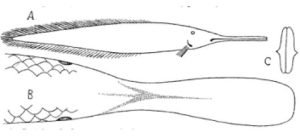
The lovely marbled lungfish from Africa:

The South American lungfish:

The Australian lungfish CHECK OUT THOSE GAMS:

Another Australian lungfish:

Further Reading:
The Hunt for the Buru by Ralph Izzard
Show Transcript:
Welcome to Strange Animals Podcast. I’m your host, Kate Shaw.
This week’s episode is about the lungfish, and I’m going in depth about some mystery lungfish later in the episode. So don’t give up on me if you think freshwater fish are boring.
Lungfish are unusual since they are fish but have lungs and can breathe air. Some fish species can get by for a short time gulping air into a modified swim bladder when water is oxygen poor, but the lungfish has real actual lungs that are more mammal-like than anything found in other fish. The ancestors of lungfish, which developed during the Devonian period nearly 400 million years ago, may have been the ancestors of modern amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals. This is still a controversial finding, but a 2017 molecular phylogenetic study identified lungfish as the closest living relatives of land animals.
Africa has four species of lungfish, from the smallest, the gilled African lungfish that only grows around 17 inches long, or about 44 cm, to the largest, the marbled lungfish, which can grow more than six and a half feet long, or two meters. They all resemble eels, with long bodies and four thin, almost thread-like fins. They mostly eat crustaceans, molluscs, and insect larvae. The adults have small gills but breathe air through their lungs exclusively.
The South American lungfish is in a separate family from the African lungfishes, but it’s very similar in most respects. It can grow over four feet long, or 125 cm, and looks like an eel at first glance. Its fins are thread-like and not very long, and while it has small gills, they’re nonfunctional in adults. It mostly eats snails and shrimp, and like the African lungfishes, its teeth are fused into tooth plates that crush the shells of its prey easily.
Baby South American and African lungfish have external gills like newts but look more like tadpoles. After a couple of months they develop the ability to breathe air.
The African and South American lungfishes live in swamps and shallow river basins, and during the dry season, the water of their homes may dry up completely. At the onset of the dry season, the lungfish burrows a foot or two deep into the mud, or 30 to 60 centimeters, and lines the burrow with mucus to keep its body from drying out. Then it curls up in the bottom of the hole and lowers its metabolism, and stays there for months until the rains return and soak its dried mud home. This is called aestivation, and it’s related to hibernation except that it usually happens in warm weather instead of cold.
The Australian lungfish, also called the Queensland lungfish, lives in Australia and retains many features that are considered primitive compared to other lungfish species. It’s so different from the other lungfish species it’s even in a different order. Let’s learn about just how different it is and why that’s important.
In 1869 a farmer visiting the Sydney Museum asked why there were no specimens displayed of a big olive-green fish from some nearby rivers. The curator, Gerard Krefft, had no idea what the guy was talking about. No problem, the guy said, or probably no worries, he’d just get his cousin to send the museum a few. Not long after, a barrel full of salted greenish fish that looked like big fat eels arrived and Krefft set about examining them.
When he saw the teeth, he practically fainted. He’d seen those teeth before—in fossils several hundred million years old. No one even knew what fish those teeth came from. And here they were again in fish that had been pulled from a local river only days before.
The Australian lungfish doesn’t have ordinary teeth, it has four tooth plates or combs that resemble regular teeth that have fused together. Its skull is also very different from all other fish, possibly because of its feeding style. It crushes its prey with its tooth combs, so its skull has to be able to withstand a lot of pressure from the force of its own bite. Other lungfish species share this trait to some degree, but with modifications that appear more recent.
The Australian lungfish lives in slow-moving rivers and deep ponds and hunts using electroreception. Larger ones mostly eat snails and crustaceans, while smaller ones also eat insect larvae and occasionally small fish. It can grow up to about five feet long, or 150 cm. Its body is covered with large overlapping scales, and its four fins look more like flippers or paddles. Its tail comes to a single rounded point. In short, it looks superficially like a coelacanth, which is not a big surprise because it’s related to the coelacanth. While the Australian lungfish doesn’t actually get out of the water and walk on its fins, it does stand on them and sometimes walks around on them underwater.
Unlike the other lungfishes, the Australian lungfish has only a single lung instead of a pair. Most of the time it breathes through its gills, but at night when it’s active, or during spawning season or other times when it needs more oxygen, it surfaces periodically to breathe. When it does so, it makes a distinctive gasping sound. During droughts when its pond or river grows shallow, an Australian lungfish can survive when other fish can’t. As long as its gills remain moist, it can survive by breathing air through its lung. But unlike other lungfish, it doesn’t aestivate in mud.
The Australian lungfish hasn’t changed appreciably for the last 100 million years. The only real change it exhibits from its ancestors 300 million years ago is that it’s not as big, since they grew some 13 feet long, or 4 meters. Lungfish used to be widespread fish that lived in freshwater back when the world’s continents were smushed together in one supercontinent called Pangaea, some 335 million years ago. When Pangaea began to break up into smaller continents about 175 million years ago, various species of lungfish remained in different parts of the world. Now we’ve only got six species left…maybe.
A lot of mysterious eel-like fish or fish-like lizard stories might refer to lungfish. Some of the mystery animals are probably extinct, whatever they were, but some might still be around. All known lungfish were only discovered by science within the last 150 years or so, and it’s quite possible more are lurking quietly in remote swamps and rivers.
That brings me to a mystery that may or may not have anything to do with the lungfish. Occasionally when I’m researching a topic for an episode, I come across something interesting that doesn’t really belong in that episode but which isn’t enough on its own for a full episode. I sometimes spin those into bonus episodes for our Patreon subscribers. That happened recently with our Brantevik eel episode, where some blue river eels took me down a research rabbit hole that had nothing to do with eels. But a mystery animal I only covered in passing in that bonus episode suddenly has new meaning for this one.
The mystery animal is the indus worm, sometimes called the scolex. We don’t know what it was, if anything. It might have been a fable that got repeated and exaggerated over the centuries. It might have been something more akin to disinformation. It might have been both.
We have the story from multiple ancient sources, back to Ctesius’s original account in the fourth century BCE. The story goes that the river Indus, which flows through modern-day China, India, and Pakistan, contained a white worm of enormous size. It was supposed to be around 7 cubits long, or 10 ½ feet, or just over three meters, but it was so big around that a ten-year-old could barely encircle it with their arms, and that’s a straight-up quote from Ctesius only not in ancient Greek. In other words, it was a big fat eel-like creature over ten feet long, white in color. Moreover, it had weird teeth. Ctesias didn’t mention the teeth, but a few hundred years later Aelian said that it had two teeth, square and about eighteen inches long, or 45 cm, which it used to catch and crush animals that it caught at night.
This is an interesting detail that points to an animal with teeth something like a lungfish. But the indus worm was also supposed to drag animals into the water when they came to the edge to drink, which sounds like a crocodile—but the ancient Greeks were familiar with crocodiles and this clearly wasn’t one. The word crocodile comes directly from Greek, in fact. But there’s one more important detail about the indus worm that changes everything.
The indus worm was supposed to be useless except for the oil it produced. Now, all animal fat produces flammable oil, but it has to be rendered first. The indus worm was full of just plain oil. According to the ancient accounts, after an indus worm was killed—not an easy thing to do, apparently, as it required dozens of men with spears and clubs to subdue—it was hung up over a vessel, and the oil allowed to drip into the vessel from the body for a full month. One indus worm would produce about 2 ½ quarts, or almost five liters of oil. The oil was so flammable that only the king of India was allowed to own it, and he used it to level cities. Not only that, but the flame it produced couldn’t be put out unless it was smothered with mud.
This sounds like a petroleum-based flame. It might even refer to Greek fire, a deadly weapon of the ancient world. We don’t know what Greek fire was made of, but it wasn’t an animal-based oil. It could be that rulers who knew the secret of producing unquenchable flame obfuscated the knowledge by telling people the oil came from a vicious animal only found in one distant river. If so, it’s possible that the indus worm wasn’t based on a real animal at all.
I can just hear the conversation that started it all. “Hey, where do you get that oil that sticks to people and burns them up even after they jump in the water?” “Oh, um, it’s really hard to get. Yeah, totally hard. You know those little white worms that sometimes get in figs? Picture one of those that’s like, ten feet long, and it only lives in one river in India…”
Anyway, we have no way of knowing whether the indus worm was a real animal. It actually sounds kind of plausible, though, especially if you assume some of the stories are either exaggerated or confused with other animals. The Indus is a really long river with a lot of unique animal species. It’s possible there was once a lungfish that grew ten feet long and had flattened tooth plates like those of South American and African lungfishes.
Then again, there is another possibility. The rare Indus river dolphin grows to about eight and a half feet long, or 2 ½ meters. I’m probably going to do an entire episode on freshwater dolphins eventually so I won’t go into too much detail about it today, but while young dolphins have pointed teeth, when the dolphin matures its teeth develop into square, flat disks. But the dolphin isn’t white, it’s brown, and no one could look at a dolphin and call it a worm.
But there are other reports of mystery fish in Asia that may be lungfish. This is where I had to stop research for this episode until I ordered, received, and read a book called The Hunt for the Buru by Ralph Izzard. If in doubt, go back to the primary sources whenever possible. Izzard was a foreign correspondent for the London Daily Mail, and in 1948 he and a photographer accompanied explorer Charles Stonor on an expedition to find what they thought might be a living dinosaur or some other reptile. But while many cryptozoologists today think the buru might be a type of monitor lizard, zoologist Karl Shuker suggests the details given in the book sound more like a type of lungfish.
Accounts of the buru were collected in an anthropological study of the Apa Tani tribe in 1945 and ’46. The Apa Tani live in a large valley in northeastern India, in the foothills of the Himalayas, and were an insular people who at the time rarely traveled away from their valley. They’re characterized in The Hunt for the Buru as intelligent and practical, but not especially creative. They have no system of reading or writing, produce no art, and are efficient and knowledgeable rice farmers. The relevant parts of the study are reproduced in The Hunt for the Buru, and I’m happy to report that this was a genuine scholarly study, not a bunch of enthusiastic amateurs asking leading questions. The buru information was only collected incidentally as part of the tribe’s history and traditions, but I suspect mostly because the anthropologists found it interesting. A quick look online for more modern information about the Apa Tani point to them being really nice people. They have a festival celebrating friendship every spring that lasts an entire month. These days they’re much more mainstream but still continue their traditional practices of farming.
According to the Apa Tani, their ancestors migrated to the valley along two rivers, and accounts of their migration match up with actual places with a high degree of accuracy even though the migration took place many centuries ago. In other words, these are people with a detailed oral history, and that’s important when we come to their accounts of the buru.
When they reached the valley, it was largely flooded with a swamp and lake. In the lake was an animal they called the buru. It wasn’t an aggressive animal. It lived in deep water but occasionally came to the surface, stuck its head above water, and made a noise translated as a hoarse bellow. Occasionally a buru would nose through the mud in shallower water, and frequently waved its head from side to side. It didn’t eat fish and was described as living on mud. It was about 4 meters long, or a bit over 13 feet, and was dark blue blotched with white, with a white belly. I’ll go into more details of its appearance in a few minutes.
The Apa Tani drained much of the swamp and lake to create more farmland for rice paddies, and on four occasions, a buru was trapped in a pool of deeper water. The Apa Tani killed the burus trapped this way and buried their bodies, and the location of the buried burus are still known. The Apa Tani reported that there were no more burus in the valley.
In 1947, Charles Stonor was traveling near the Apa Tani’s valley and asked a member of a different tribe if he’d ever heard of the buru. Stonor apparently was both a trained zoologist and had at least some background in anthropology, according to Izzard. To Stonor’s surprise, the man said he not only knew about the buru, but said it lived in a swamp not too far away, called Rilo. Naturally Stonor decided to visit, and when he spoke to the nearby villagers, they said the buru did indeed live in the swamp.
Stonor recorded their accounts of the animal. It lives underwater and only comes to the surface briefly—“every now and again they come up above the surface. When one of them comes up there is a great disturbance and splashing, and the beast comes straight up out of the water, stays for a few moments only, and then disappears down again.” The buru were described as black and white, with a head as large as a bison’s but with a longer snout, and with a pair of small backwards-pointing horns. The buru was only seen in summer, when the swamp floods and becomes a lake. But no one in the Rilo village had ever seen a buru up close.
In early 1948 Izzard heard about the buru from a friend, and approached Stonor to ask if he wanted to undertake a small expedition to look for it. Stonor agreed, and in April 1948 the expedition headed out on the search.
They… didn’t find any burus. Spoiler alert: after months of careful daily watches of the swamp, they decided the buru had possibly once lived in the valley, but was now extinct, and since it had never been an animal the villagers paid much attention to, no one had realized it was gone. This sounds absurd until you realize that the village had only been settled about a decade before. Many trees had been felled, which increased erosion so that the swamp had silted up considerably and was no longer very deep even at full flood. It’s possible that the burus had died due to these changing conditions, especially if they hadn’t been very numerous to start with.
The expedition returned to civilization only to find that rumors of the buru hunt had leaked, and the papers were full of reports of a 90-foot “dinotherium” sighted in the jungle.
I find it interesting that Izzard rejected the idea that the buru was a lungfish, because, he writes, “no known fish would expose itself above water, for no practical purpose, for such a length of time.” Presumably Izzard didn’t realize that lungfish actually use their lungs to breathe air, and that they must surface briefly to do so.
So was the buru reported in the Rilo swamp the same buru that had once lived in the Apa Tani valley? Probably not. Izzard notes that while the two valleys are relatively close to each other, he does point out that they were completely separated by a ridge of mountains. Even if both burus were the same kind of animal, they were probably different subspecies at the very least considering how long the two populations must have been separated.
Let’s return to the Apa Tani buru, since the reports gathered from the mid-1940s anthropological study are clear and detailed compared to the Rilo buru reports.
The Apa Tani buru had limbs, but while some reports called them short legs that somewhat resembled mole forelegs with claws used for digging, one old man stubbornly refused to describe them as legs. The anthropologists found this confusing because they assumed he was talking about a reptile. I’ll quote from the relevant sections of the report. The old man was named Tamar.
“ ‘The buru was long: it had a long tail with flanges on the sides: they lay along it when resting, but were pushed out sideways when the beast was moving: it could twist its tail round and catch anything with it.’ The flanges were demonstrated by holding a piece of paper against a stick. We use the word ‘flange’ for want of a better expression. Tamar described them as pieces fastened on the sides of the tail. …
Q What sort of legs did it have?
A ‘It had no legs: the body was like a snake.’ Tamar then described and demonstrated that the tail flanges were grouped in two pairs, were about 50 cm long, and were as thick as a man’s arm: he added they were used in burrowing. We got the impression that he was trying to convey the meaning that they were appendages, but not limbs in the true sense of the word.”
I wonder if he was trying to explain, through an interpreter, something he himself probably didn’t fully understand, lobed fins. The Australian lungfish’s lobed fins do look like stubby legs with a frill around them that could be taken to be claws.
Tamar also described the buru as a snake-like creature. He said its head was like a snake’s with a long snout and that it had three hard plates on its head that helped it burrow into the mud. And like the other reports, he said it ate mud, not fish or animals.
This sounds a lot like a lungfish, which eats crustaceans and snails it digs out of the mud. Admittedly Tamar also said it had a forked tongue, which is not a lungfish trait. Many cryptozoologists think this forked tongue points to a type of monitor lizard, but while some monitor lizard species do spend a lot of time in the water, notably the widespread Asian monitor lizard, the buru is described as being exclusively aquatic. Monitor lizards also are very lizardy, with large, strong legs. And monitor lizards don’t stay in the mud when a swamp dries up.
To me, all this paints a picture of a large lungfish, blue and white in color, with lobed fins like an Australian lungfish and probably working gills as well as a lung or pair of lungs. It may have aestivated in the mud like African and South American lungfish during the dry season, and during the rainy season when it was spawning, it might have needed to breathe at the surface like the Australian lungfish to give it more oxygen than its gills could manage on their own.
Hopefully someone’s out there looking for burus in other remote swamps of Asia. I can’t do it myself. I’m busy.
There are brief anecdotal reports of possible new species of lungfish in Asia, Africa, and South America, although with very little to go on. But I wouldn’t be one bit surprised if someone discovered another lungfish species in a hard-to-reach swamp one of these days. Those 400-million-year-old fish are survivors.
You can find Strange Animals Podcast online at strangeanimalspodcast.com. We’re on Twitter at strangebeasties and have a facebook page at facebook.com/strangeanimalspodcast. If you have questions, comments, or suggestions for future episodes, email us at strangeanimalspodcast@gmail.com. If you like the podcast and want to help us out, leave us a rating and review on Apple Podcasts or whatever platform you listen on. We also have a Patreon if you’d like to support us that way.
Thanks for listening!