Podcast: Play in new window | Download (Duration: 18:48 — 18.8MB)
Subscribe: | More
This week we’re taking a bunch of listener suggestions and learning about a bunch of amazing hoofed animals! Thanks to Richard E., Pranav, Grady, and Simon for all their suggestions!
A pronghorn antelope, which is NEITHER AN ANTELOPE NOR A DEER:

A musk deer, which is NOT ACTUALLY A DEER AND ACTUALLY LOOKS A LOT LIKE A KANGAROO OR RABBIT WITH FANGS:


A chevrotain, or mouse deer, which is ALSO NOT A DEER AND LOOKS LIKE A RODENT FRANKLY (lesser mouse deer on left, water chevrotain on right)


A mama pudu with her baby, WHICH ARE DEER:

A goat eating poison ivy like I told you they do:

A horse eating watermelon, because it’s adorable:

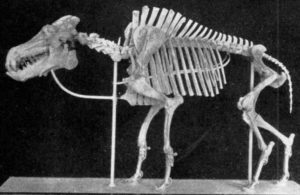
An entelodont, AKA HELL PIG:
Show transcript:
Welcome to Strange Animals Podcast. I’m your host, Kate Shaw.
This week I wanted to get back into some of the excellent suggestions I’ve gotten from listeners. I looked over the list, hoping that a theme would present itself…and one did. Sort of. This week let’s learn about some interesting hoofed animals, some of them living today, some extinct. Thanks to Richard E., Grady, Pranav, and Simon for the suggestions I used in this episode, in no particular order.
First, Richard asked about the differences between deer and antelope. This is an excellent question, obviously, because I’ve been sitting here staring at the screen thinking, “Well, I know they’re not members of the same family but how closely are they related?” So let’s find out. And I’ll warn you now, this gets complicated—but in an interesting way.
Antelopes are bovids, related to cows, sheep, and goats. Deer are cervids. Both groups are related, but not very closely. They’re both members of the order Artiodactyla, the even-toed ungulates, because they have hooves with two toes, called cloven hooves.
At first glance, many antelopes look a lot like deer. But antelopes have horns, not antlers, and the horns are permanent. Deer have antlers, which they shed and regrow every year. And antelope horns, like the horns of goats, sheep, and cattle, don’t branch, whereas deer antlers almost always do.
So far this is pretty straightforward. But now things get complicated. Antelopes are native to Africa and Eurasia while deer live throughout the world. But there are deer that aren’t deer and there are some antelopes that aren’t antelopes. Uh oh. We’d better figure this out.
One thing to remember is that the group of bovids referred to as antelopes have all been lumped together in what’s sometimes referred to as a wastebasket taxon. Basically that means that the animals in that taxon didn’t really fit anywhere else, so scientists grouped them together for the time being. If a bovid is clearly not a cow, a sheep, or a goat, it’s put in the antelope group.
There aren’t any antelopes living in the Americas today. If you happen to live in the western part of North America, you probably just sat up and said, “Hey, you forgot about the pronghorn!” But the pronghorn antelope…is not an antelope.
Sure, the pronghorn looks like an antelope. It’s deer-like, runs extremely fast just like antelopes, and has short black horns. But look at those horns. It’s called a pronghorn because the horns of the males have a prong, or branch, so that the horn is shaped sort of like a Y, with the front branch of the Y shorter than the other, and the longer branch of the Y having a sort of hook at the top. Remember how antelopes only ever have unbranched horns? That’s a clue that the pronghorn isn’t an antelope.
But the pronghorn also isn’t a deer. Its horns are horns, not antlers, and it keeps its horns throughout its life instead of shedding them every year. Except that it kind of does shed part of the horn every year, the sheath. The inside of a horn is bone that grows from the skull, but a sheath of keratin grows over it. If you’ve ever seen an old-fashioned drinking cup made of horn, it was made of a horn sheath, usually from a bull. Most horned animals keep the sheath, which grows as the horn grows underneath, but the pronghorn male sheds the sheath of his horns every year and then grows new ones.
So what is the pronghorn related to? Are you ready? It’s related to the giraffe! I’m not even making this up. It’s not closely related to the giraffe, though, and it’s the only living member of its own family. I think I might have to revisit the pronghorn family in its own episode one day, so for now I’ll just point out that the pronghorn is the second-fastest land animal alive, with only the cheetah able to run faster. The pronghorn can run 55 mph, or 88 km/h, for half a mile, or .8 km.
So the pronghorn isn’t an antelope or a bovid, but it looks like an antelope because it shares a similar habitat and ecological niche. You know what that means! Yes, the pronghorn looks like an antelope due to convergent evolution.
Next, let’s talk about those deer that aren’t deer. Are they related to giraffes too? Are giraffe relatives taking over? No and probably no.
There are two groups of deer that aren’t actually deer. The musk deer of Asia and the chevrotains of Asia and Africa are related to deer but they’re also related about as closely to bovids like antelopes. They’re also not that closely related to each other. Just looking at them tells you that they’re different, since they don’t look like ordinary deer.
There are seven species of musk deer alive today, and while musk deer used to live throughout Eurasia, these days they’re restricted to Asia, especially the Himalayas. They’re small, no more than two and a half feet high at the shoulder, or 70 cm, with hind legs that are longer than their front legs. The back is humped more like a rabbit’s than a deer’s. This allows them to run extremely quickly. They also don’t have antlers or horns, but males do have fangs that they use to fight other males. Fangs, people! Deer-like animals with fangs! They’re not small fangs, either, they’re basically slender tusks that grow down from the upper jaw and can be up to four inches long, or 10 cm. The tusks break easily, but they grow continuously, especially during mating season.
All species of musk deer are endangered due to overhunting, especially for the male’s scent gland, called a musk gland. This gland has been used in perfumes for centuries. These days most perfume-makers use a synthetic musk instead, but the musk deer is still being hunted for its musk gland. The male uses his musk to mark his territory, which warns other males away and attracts females.
Musk deer kind of look like if you tried to draw a kangaroo but you got mixed up halfway through and forgot you were drawing a kangaroo and decided to draw a rabbit instead. Then you added fangs.
The other deer that isn’t a deer is the chevrotain, also called the mouse-deer. There are a number of chevrotain species and they all look more like little rodents than deer. They’re all small and have bulky, rounded bodies but short spindly legs. Like musk deer they have long canine teeth instead of horns or antlers. Female chevrotains have these fangs too, but they’re longer in males and are angled outward like tiny pig tusks. Males use the teeth to fight each other. Most chevrotains are brown or reddish-brown with white streaks on the throat and sometimes face.
Some species of chevrotain like water and, like the marsh cottontail rabbit we learned about last week, will submerge in the water to hide from predators. It can hold its breath for up to four minutes. It can even walk on the bottom of the stream bed, grabbing plants with its teeth to help keep it from being swept away by the current.
The smallest chevrotain is the lesser mouse-deer, which lives across southeast Asia. It’s only about 18 inches tall at most, or 45 cm, and weighs less than 5 pounds, or 2 kg. But the smallest deer was a suggestion by Simon, and that’s the pudu. Specifically, it’s the northern pudu with the scientific name Pudu mephistophiles. I don’t know how it got this name since it’s only 14 inches tall, or 35 cm, and looks inoffensive and not devilish at all. It’s reddish-brown with big eyes, rounded ears, and little stubby antlers that only grow around four inches long, or 10 cm. It lives at high altitudes in the Andes Mountains in South America. It sheds its tiny antlers every year and regrows them, but unlike most other deer, its antlers don’t have any branches.
Because the pudu is so small, it can have trouble reaching the plants it eats. Like other deer, it’s a browser instead of a grazer, eating leaves, twigs, fruit, seeds, and bark, but not grass. It stands on its hind legs to reach leaves, but if it finds a bendy sapling, it will push it with its forelegs until the tree is bent down far enough for the pudu to reach its leaves and twigs.
The pudu is territorial and travels on little trails it makes through its territory. The southern pudu, which is only slightly larger than the northern pudu, will also build tunnels in the underbrush so it can travel without being seen by predators.
Unlike the pudu, the chevrotain hasn’t changed much in millions of years and shows primitive traits compared to modern hoofed animals. It actually shares some traits in common with pigs. While pigs are hoofed animals, they’re not closely related to chevrotains. Researchers think the chevrotain retains traits that were once common in early ruminants.
What’s a ruminant, you may be asking. Aha, this is a good question. Ruminants are hoofed animals that chew their cud, and that includes the chevrotain, the giraffe, musk deer, deer, bovids like cows, goats, sheep, and antelopes, and the pronghorn.
As I mentioned last week in the giant rabbits episode, cud-chewing is one way some animals have evolved to extract as many nutrients as possible from plants. Most plant material is tough and can be hard to digest. Ruminants have a complicated digestive system that helps with this. I bet someone at some point has told you that cows have four stomachs, and maybe you didn’t believe them. But they do. Almost all ruminants have four stomachs, or more properly, four specialized chambers that make up the stomach section of the digestive system.
This is how it works. Let’s say a goat is eating poison ivy leaves, which is something they do, and they don’t seem to have any problem with it either. The goat swallows the leaves, which go into the first two chambers of the goat’s stomach, called the rumen and the reticulum. Both these chambers contain lots of beneficial microbes and bacteria, which immediately start to ferment and break down the leaves. As this happens, the food forms into clumps of partly digested leaves called cuds. After a while, the goat regurgitates a cud and chews it thoroughly, further breaking it down, then swallows it and regurgitates another cud to do the same thing, and so on until it’s cudded everything in its rumen. Then it goes to eat some more.
After the cuds have been chewed and swallowed again, they pass through the rumen and reticulum and into the third chamber, the omasum [oh-MAY-sum]. This is where nutrients start to be absorbed. Only tiny pieces of plant are able to pass through the omasum into the fourth chamber, the abomasum [abba-MAY-sum], which is equivalent to our own stomach. This chamber adds acids to the plant material and kicks the digestive process into high gear, pushing everything on into the small intestine, where most of the nutrients are absorbed. Then what’s left of the plants goes on into the large intestine, where water is absorbed from it and the indigestible parts are packed into pellets that are pooped out.
So most ruminants have four-chambered stomachs. But not all of them. You know which ruminant only has three stomachs? That’s right, the chevrotain, the little mouse deer that kind of looks like a pig.
Pigs, by the way, aren’t ruminants. They’re omnivores and only have one stomach.
So with all this information about chewing cuds in your brain, let’s answer Grady’s question. Grady wants to know how horses digest their food.
Are horses ruminants? They eat grass and other plants. The answer is no, horses aren’t ruminants and don’t chew their cud as part of the digestive process. A horse has only one stomach but it still manages to digest grass and other tough plants just fine. This is how it works.
First, the horse chews its food really thoroughly before swallowing. Like ruminants, the horse’s teeth continue to grow throughout its life, since plants wear teeth down. The horse also produces massive amounts of saliva as it chews, and saliva contains an enzyme called amylase that helps start the digestive process. So before a horse even swallows a single bite of grass or hay, that plant material is chewed up into little bits and mixed with lots of saliva.
Oh, in case you were wondering, a male horse has forty teeth while a female only has 36. I do not know why. But ruminants don’t have front top teeth at all, just a bony pad. That helps them trim plants right down to the ground.
After a horse swallows its food, the stomach mixes it with digestive enzymes and acids that break the plant material down even more. A horse actually has a surprisingly small stomach for its body size, but typically food doesn’t stay in the stomach long. It passes into the small intestine and then into the large intestine, where most of the actual digestion takes place. Microbes in the large intestine help break down the plant material so that the horse can absorb it.
The large intestine is sometimes called the hindgut, because it’s behind the other parts of the digestive system. Horses are hindgut fermenters, which means a horse’s food is fermented, or broken down by microbes, in the hindgut, or large intestine. Ruminants are called foregut fermenters because their food is fermented, or broken down by microbes, in the foregut, or the stomach chambers that come before the rest of the digestive system. And if you’re curious, rabbits and hares are also considered hindgut fermenters.
There are lots more fascinating hoofed animals I want to talk about, but I have to stop somewhere. Don’t worry, eventually we’ll learn about some actual deer with fangs as well as antlers, and more about the pronghorn, and lots more. But we’ll finish up this week with a suggestion from Pranav, who wanted to learn about an extinct hoofed animal called the entelodont.
What’s an entelodont? It’s sometimes called the HELL PIG. Why would it be called that? Is it like the little Mephistopheles pudu who must have scared some scientist one day and ended up with a devilish name? Nope, the entelodont is called the hell pig because it was enormous and terrifying. Fortunately for us, it went extinct millions of years ago.
Despite its name, the entelodont isn’t all that closely related to the pig. It’s more closely related to the hippo and to WHALES, because whales and hippos are closely related. But the various species of entelodont were pig-like in many ways. Entelodonts lived throughout much of the world, but let’s look specifically at the biggest entelodont known, Daeodon [DIE-oh-don], which lived in North America up to about 18 million years ago.
Daeodon stood nearly six feet tall at the shoulder, or about 1.8 meters. It had long, slender legs with cloven hooves, and its body was bulky and something like 10 feet long, or 3 meters. It didn’t have a pig-like snout, and in fact its nostrils were on the sides of its nose, which probably helped it track food by scent. It had flared cheekbones with bony protrusions that probably meant it looked a lot like a modern warthog. Its tail was short and small.
Daeodon was an omnivore, which means it would eat just about anything it wanted, and it had the sharp, serrated teeth of a predator. It probably did a lot of scavenging of dead animals, but it could have hunted and killed prey too. Its jaw was so strong it could bite right through bones. And it could run quickly.
So basically, daeodon and entelodonts in general earn the nickname hell pig. It’s probably a good thing they’re not still around. I personally prefer the tiny and harmless Pudu mephistophiles.
You can find Strange Animals Podcast online at strangeanimalspodcast.com. We’re on Twitter at strangebeasties and have a facebook page at facebook.com/strangeanimalspodcast. If you have questions, comments, or suggestions for future episodes, email us at strangeanimalspodcast@gmail.com. We also have a Patreon if you’d like to support us that way.
Thanks for listening!










