Podcast: Play in new window | Download (Duration: 9:49 — 11.0MB)
Thanks to Zachary and Anbo for their suggestions this week! Let’s learn about some shrimp!
Further reading:
This is why the pistol shrimp is immune to its own powerful shock waves
The Symbiotic Relationship Between Gobies and Pistol Shrimp
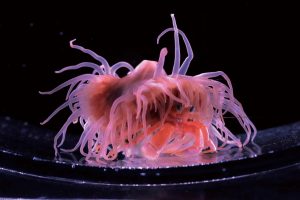
An eastern ghost shrimp:

A snapping shrimp:

A goby fish and its snapping shrimp buddy:

Show transcript:
Welcome to Strange Animals Podcast. I’m your host, Kate Shaw.
This week we’re going to have an episode about a few different types of shrimp, with suggestions from Zachary and Ambo.
Let’s start with the ghost shrimp, since Zachary recently got an aquarium and has some ghost shrimp in it.
The name ghost shrimp refers to various species of freshwater shrimp in the genus Palaemon. One of the most popular species to keep as a pet is Palaemonetes paludosus. It’s sometimes called the glass shrimp since it’s mostly transparent, or the eastern ghost shrimp.
The eastern ghost shrimp can grow up to about an inch long, or 2.5 cm. It’s native to the southeastern United States, mostly east of the Appalachian Mountains, where it lives in lakes and eats plankton.
Even though the eastern ghost shrimp is mostly transparent, it can actually change its color to blend in with its background. Only one other species of ghost shrimp is known to do this, a very similar species that is only found in the Mississippi River.
There are dozens of species of ghost shrimp, though, and they live throughout the world. Some species are freshwater, others are marine. Most are at least partially transparent and rarely grow more than two inches long, or maybe 5 cm at most. In some cases people catch them to eat, although more often they’re caught to use as bait or fish food, and of course they’re eaten by a whole lot of wild animals.
We actually don’t know a whole lot about many species of ghost shrimp. Some have only recently been discovered, and some are endangered. For instance, the Florida cave shrimp is only found in a single sinkhole near Gainesville, Florida. It’s the only known species of ghost shrimp that lives in a cave, and it’s closely related to the eastern ghost shrimp.
The Florida cave shrimp grows a little over one inch long, or about 3 cm. It has eyes but doesn’t need them, so they don’t work anymore. It’s mostly transparent with some white spots. It was discovered in 1953 during a scientific exploration of a sinkhole in the Squirrel Chimney Cave and hasn’t been seen since 1973. It may even be extinct by now, but further explorations of the sinkhole have revealed that it connects with a much larger underwater cave system. Hopefully the little shrimp lives within this cave system, but it hasn’t been found anywhere else so far and we know almost nothing about it.
That’s pretty much all there is to know about the ghost shrimp, so congratulations to Zachary for keeping a mysterious little friend in your aquarium.
Next, Anbo wanted to learn about snapping shrimp. (Anbo also wanted to learn about the mantis shrimp, but it turns out that the mantis shrimp isn’t actually a shrimp, or a mantis, and it deserves its own episode one day.) We talked about the snapping shrimp before in episode 273, but there’s definitely more to learn about it. There are a whole lot of species–like, more than a thousand. They’re especially common in coral reefs and live in colonies that communicate with each other by snapping their claws. The sound is so loud that it can sound like a gunshot, which is why it’s sometimes called the pistol shrimp.
The snapping shrimp is about the same size as the ghost shrimp, about 2 inches long at most, or 5 cm. One of its claws is ordinary, but the other claw is much bigger, and it’s the large claw that makes the snapping sound. As we discussed in episode 273, the snapping shrimp will hide in a burrow or rock crevice with its antennae sticking out, and when a small animal like a fish happens by, the shrimp will emerge from its hiding place just far enough to get a good shot at the animal. It opens its big claw and snaps it shut so fast and so forcefully that it shoots tiny bubbles out at speeds of over 60mph, or 100 km/hour. The bubbles only travel a few millimeters in distance, but the shock wave is powerful enough at this short range to stun or outright kill a small animal.
Scientists figured out how the snapping shrimp’s snap worked in 2020, but it wasn’t until 2022 that they discovered why the shrimp doesn’t damage its tiny shrimp brain when it snaps. It turns out that its brain is protected by a translucent helmet called an orbital hood. It needs to be translucent because it covers the shrimp’s eyes as well as the rest of its head. The hood is an extension of the shrimp’s exoskeleton, and it has an opening at the back. Scientists think that when the shock wave of a snap meets the hood, the change in water pressure under the hood is expelled out the opening instead of affecting the brain.
Scientists want to learn how exactly the orbital hood works to redirect pressure waves, in hopes of being able to replicate it. That way we can make really effective armor for people who work with explosives, or for military personnel.
In episode 332 we talked about mutualism, and the snapping shrimp actually has a mutualistic relationship with the goby fish. Gobies are little fish that are usually even smaller than snapping shrimp, or not much bigger. The order Gobiiformes is one of the largest fish families, and we’ve talked about at least one type of goby before. That was back in episode 189 when we learned about the lumpsucker. Not all gobies are buddies with snapping shrimp, but about 130 species are, most of which live in the Pacific Ocean.
Snapping shrimp live in burrows, and the 20 species or so of snapping shrimp that partner with gobies will dig an extra-large burrow. That’s because it’s making room for its goby friend, or even more than one goby friend. The burrow can extend as much as two feet deep, or about 61 cm, with different chambers. While the shrimp is digging the burrow, the goby watches for danger. If a predator approaches, the fish warns the shrimp by moving its fins in a specific way, which signals that the shrimp should hide. If part of the burrow collapses and buries the fish, it just waits until the shrimp digs it out of the sand.
The shrimp and the goby live together in the burrow. They leave the burrow together so they can watch out for each other. The snapping shrimp doesn’t see very well so while it’s outside of the burrow, it will keep track of the goby with its long antennae. The goby watches out for danger and warns the shrimp if it needs to hide.
Both eat small animals, but the shrimp also likes eating some types of algae that grow on rocks. The shrimp will even bring pieces of algae to its burrow to snack on later, and at least one researcher has witnessed the goby help transport algae to the burrow.
During mating season, the goby brings its mate into the burrow, where the female lays eggs in the male’s chamber. Only the male takes care of the eggs, and he spends almost all of his time guarding them and swimming around them to keep them oxygenated. When he has to leave, he blocks the entrance with sand. The eggs hatch after a little over a week and the larvae swim out of the burrow immediately. The female shrimp carries her eggs around until they hatch, which they do in the burrow, and they too leave the burrow right away and float off on their own.
Both the goby eggs and the shrimp eggs hatch at night or sometimes early in the morning, which is important because those are times when both the goby and the shrimp are not active. In other words, that’s a time when the larva can safely leave the burrow without being eaten by its parent’s roommate. Having a buddy is great, but when it comes to your kids, it’s always safety first, even among fish and snapping shrimp.
You can find Strange Animals Podcast at strangeanimalspodcast.blubrry.net. That’s blueberry without any E’s. If you have questions, comments, or suggestions for future episodes, email us at strangeanimalspodcast@gmail.com. If you like the podcast and want to help us out, leave us a rating and review on Apple Podcasts or Podchaser, or just tell a friend. We also have a Patreon at patreon.com/strangeanimalspodcast if you’d like to support us for as little as one dollar a month and get monthly bonus episodes.
Thanks for listening!