Podcast: Play in new window | Download (Duration: 14:49 — 17.2MB)
It’s the second annual discoveries episode! Lots of animals new to science were described in 2021 so let’s find out about some of them.
Further reading:
First description of a new octopus species without using a scalpel
Marine Biologists Discover New Species of Octopus
Bleating or screaming? Two new, very loud, frog species described in eastern Australia
Meet the freaky fanged frog from the Philippines
New alpine moth solves a 180-year-old mystery
Meet the latest member of Hokie Nation, a newly discovered millipede that lives at Virginia Tech
Fourteen new species of shrew found on Indonesian island
New beautiful, dragon-like species of lizard discovered in the Tropical Andes
Newly discovered whale species—introducing Ramari’s beaked whale (Mesoplodon eueu)!
Scientists describe a new Himalayan snake species found via Instagram
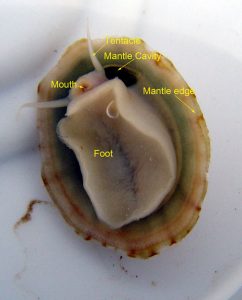
The emperor dumbo octopus (deceased):
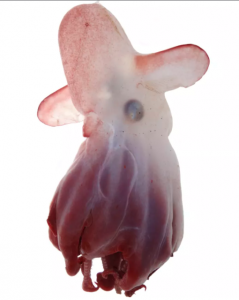
The star octopus:

New frog just dropped (that’s actually the robust bleating tree frog, already known):

The slender bleating tree frog:

The screaming tree frog:

The Mindoro fanged frog:

Some frogs do have lil bitty fangs:

The hidden Alpine moth, mystery solver:

The Hokie twisted-claw millipede:

One of 14 new species of shrew:

The snake picture that led to a discovery:

Show transcript:
Welcome to Strange Animals Podcast. I’m your host, Kate Shaw.
This episode marks our 5th year anniversary! I also finally got the ebook download codes sent to everyone who backed the Kickstarter at that level. The paperback and hardback books will hopefully be ready for me to order by the end of February and I can get them mailed out to backers as soon as humanly possible. Then I’ll focus on the audiobook! A few Kickstarter backers still haven’t responded to the survey, either with their mailing address for a physical book or for names and birthdays for the birthday shout-outs, so if that’s you, please get that information to me!
Anyway, happy birthday to Strange Animals Podcast and let’s learn about some animals new to science in 2021!
It’s easy to think that with all the animals already known, and all the people in the world, surely there aren’t very many new animals that haven’t been discovered yet. But the world is a really big place and parts of it, especially the oceans, have hardly been explored by scientists.
It can be confusing to talk about when an animal was discovered because there are multiple parts to a scientific discovery. The first part is actually finding an animal that the field scientists think might be new to science. Then they have to study the animal and compare it to known animals to determine whether it can be considered a new species or subspecies. Then they ultimately need to publish an official scientific description and give the new animal a scientific name. This process often takes years.
That’s what happened with the emperor dumbo octopus, which was first discovered in 2016. Only one individual was captured by a deep-sea rover and unfortunately it didn’t survive being brought to the surface. Instead of dissecting the body to study the internal organs, because it’s so rare, the research team decided to make a detailed 3D scan of the octopus’s body instead and see if that gave them enough information.
They approached a German medical center that specializes in brain and neurological issues, who agreed to make a scan of the octopus. It turned out that the scan was so detailed and clear that it actually worked better than dissection, plus it was non-invasive so the preserved octopus body is still intact and can be studied by other scientists. Not only that, the scan is available online for other scientists to study without them having to travel to Germany.
The emperor dumbo octopus grows around a foot long, or 30 cm, and has large fins on the sides of its mantle that look like elephant ears. There are 45 species of dumbo octopus known and obviously, more are still being discovered. They’re all deep-sea octopuses. This one was found near the sea floor almost 2.5 miles below the surface, or 4,000 meters. It was described in April of 2021 as Grimpoteuthis imperator.
Oh, and here’s a small correction from the octopus episode from a few years ago. When I was talking about different ways of pluralizing the word octopus, I mispronounced the word octopodes. It’s oc-TOP-uh-deez, not oc-tuh-podes.
Another octopus discovered in 2021 is called the star octopus that has a mantle length up to 7 inches long, or 18 cm. It lives off the southwestern coast of Australia in shallow water and is very common. It’s even caught by a local sustainable fishery. The problem is that it looks very similar to another common octopus, the gloomy octopus. The main difference is that the gloomy octopus is mostly gray or brown with rusty-red on its arms, while the star octopus is more of a yellowy-brown in color. Since individual octopuses show a lot of variation in coloration and pattern, no one noticed the difference until a recent genetic study of gloomy octopuses. The star octopus was described in November 2021 as Octopus djinda, where “djinda” is the word for star in the Nyoongar language of the area.
A study of the bleating tree frog in eastern Australia also led to a new discovery. The bleating tree frog is an incredibly loud little frog, but an analysis of sound recordings revealed that not all the calls were from the same type of frog. In fact, in addition to the bleating tree frog, there are two other really loud frog species in the same area. They look very similar but genetically they’re separate species. The two new species were described in November 2021 as the screaming tree frog and the slender bleating tree frog.
This is what the slender bleating tree frog sounds like:
[frog call]
This is what the screaming tree frog sounds like:
[another frog call]
Another newly discovered frog hiding in plain sight is the Mindoro fanged frog, found on Mindoro Island in the Philippines. It looks identical to the Acanth’s fanged frog on another island but its mating call is slightly different. That prompted scientists to use both acoustic tests of its calls and genetic tests of both frogs to determine that they are indeed separate species.
Lots of insects were discovered last year too. One of those, the hidden alpine moth, ended up solving a 180-year-old scientific mystery that no one even realized was a mystery.
The moth was actually discovered in the 1990s by researchers who were pretty sure it was a new species. It’s a diurnal moth, meaning it’s active during the day, and it lives throughout parts of the Alps. Its wingspan is up to 16mm and it’s mostly brown and silver.
Before they could describe it as a new species and give it a scientific name, the scientists had to make absolutely sure it hadn’t already been named. There are around 5,000 species of moth known to science that live in the Alps, many of them rare. The researchers narrowed it down finally to six little-known species, any one of which might turn out to be the same moth as the one they’d found.
Then they had to find specimens of those six species collected by earlier scientists, which meant hunting through the collections of different museums throughout Europe. Museums never have all their items on display at any given time. There’s always a lot of stuff in storage waiting for further study, and the larger a museum, the more stuff in storage it has. Finding one specific little moth can be difficult.
Finally, though, the scientists got all six of the other moth species together. When they sat down to examine and compare them to their new moth, they got a real surprise.
All six moths were actually the same species of moth, Dichrorampha alpestrana, described in 1843. They’d all been misidentified as new species and given new names over the last century and a half. But the new moth was different and at long last, in July 2021, it was named Dichrorampha velata. And those other six species were stricken from the record! Denied!
You don’t necessarily need to travel to remote places to find an animal new to science. A professor of taxonomy at Virginia Tech, a college in the eastern United States, turned over a rock by the campus’s duck pond and discovered a new species of millipede. It’s about three quarters of an inch long, or 2 cm, and is mostly a dark maroon in color. It’s called the Hokie twisted-claw millipede.
Meanwhile, on the other side of the world on the island of Sulawesi, a team of scientists discovered FOURTEEN different species of shrew, all described in one paper at the end of December 2021. Fourteen! It’s the largest number of new mammals described at the same time since 1931. The inventory of shrews living on Sulawesi took about a decade so it’s not like they found them all at once, but it was still confusing trying to figure out what animal belonged to a known species and what animal might belong to a new species. Sulawesi already had 7 known species of shrew and now it has 21 in all.
Shrews are small mammals that mostly eat insects and are most closely related to moles and hedgehogs. Once you add the 14 new species, there are 461 known species of shrew living in the world, and odds are good there are more just waiting to be discovered. Probably not on Sulawesi, though. I think they got them all this time.
In South America, researchers in central Peru found a new species of wood lizard that they were finally able to describe in September 2021 after extensive field studies. It’s called the Feiruz wood lizard and it lives in the tropical Andes in forested areas near the Huallaga River. It’s related to iguanas and has a spiny crest down its neck and the upper part of its back. The females are usually a soft brown or green but males are brighter and vary in color from green to orangey-brown to gray, and males also have spots on their sides.
The Feiruz wood lizard’s habitat is fragmented and increasingly threatened by development, although some of the lizards do live in a national park. Researchers have also found a lot of other animals and plants new to science in the area, so hopefully it can be protected soon.
So far, all the animals we’ve talked about have been small. What about big animals? Well, in October 2021 a new whale was described. Is that big enough for you? It’s not even the same new whale we talked about in last year’s discoveries episode.
The new whale is called Mesoplodon eueu, or Ramari’s beaked whale. It’s been known about for a while but scientists thought it was a population of True’s beaked whale that lives in the Indian Ocean instead of the Atlantic.
When a dead whale washed ashore on the South Island of New Zealand in 2011, it was initially identified as a True’s beaked whale. A Mātauranga Māori whale expert named Ramari Stewart wasn’t so sure, though. She thought it looked different than a True’s beaked whale. She got together with marine biologist Emma Carroll to study the whale and compare it to True’s beaked whale, which took a while since we don’t actually know very much about True’s beaked whale either.
The end result, though, is that the new whale is indeed a new species. It grows around 18 feet long, or 5.5 meters, and probably lives in the open ocean where it dives deeply to find food.
We could go on and on because so many animals were discovered last year, but let’s finish with a fun one from India. In June of 2020, a graduate student named Virender Bhardwaj was stuck at home during lockdowns. He was able to go on walks, so he took pictures of interesting things he saw and posted them online. One day he posted a picture of a common local snake called the kukri snake.
A herpetologist at India’s National Centre for Biological Sciences noticed the picture and immediately suspected it wasn’t a known species of kukri snake. He contacted Bhardwaj to see where he’d found the snake, and by the end of the month Bhardwaj had managed to catch two of them. Genetic analysis was delayed because of the lockdowns, but they described it in December of 2021 as the Churah Valley kukri snake.
The new snake is stripey and grows over a foot long, or 30 cm. It probably mostly eats eggs.
It just goes to show, no matter where you live, you might be the one to find a new species of animal. Learn all you can about your local animals so that if you see one that doesn’t quite match what you expect, you can take pictures and contact an expert. Maybe next year I’ll be talking about your discovery.
You can find Strange Animals Podcast at strangeanimalspodcast.blubrry.net. That’s blueberry without any E’s. If you have questions, comments, or suggestions for future episodes, email us at strangeanimalspodcast@gmail.com. If you like the podcast and want to help us out, leave us a rating and review on Apple Podcasts or Podchaser, or just tell a friend. We also have a Patreon at patreon.com/strangeanimalspodcast if you’d like to support us for as little as one dollar a month and get monthly bonus episodes.
Thanks for listening!