Podcast: Play in new window | Download (Duration: 17:28 — 20.2MB)
Let’s learn about some of the animals discovered in 2022! There are lots, so let’s go!
Further Reading:
In Japanese waters, a newly described anemone lives on the back of a hermit crab
Rare ‘fossil’ clam discovered alive
Marine Biologists Discover New Giant Isopod
Mysterious ‘blue goo’ at the bottom of the sea stumps scientists
New Species of Mossy Frog Discovered in Vietnam
A Wildlife YouTuber Discovered This New Species of Tarantula in Thailand
Meet Nepenthes pudica, Carnivorous Plant that Produces Underground Traps
Scientists discover shark graveyard at the bottom of the ocean
Further Watching:
JoCho Sippawat’s YouTube channel
A newly discovered sea anemone (photo by Akihiro Yoshikawa):
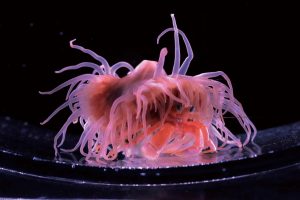
A mysterious blue blob seen by a deep-sea rover:

A newly discovered frog:

A newly discovered tarantula (photo by JoCho Sippawat):

Show transcript:
Welcome to Strange Animals Podcast. I’m your host, Kate Shaw.
It’s the 2022 discoveries episode, where we learn about some of the animals discovered in 2022! Most of the time these animals were actually discovered by scientists before 2022, but the description was published in that year so that’s when we first learned about them. And, of course, a lot of these animals were already known to the local people but had never been studied by scientists before. There are lots of animals in the world but not that many scientists.
The great thing is, so many animals get discovered in any given year that I have to pick and choose the ones I think listeners will find most interesting, which in a stunning coincidence turns out to be the ones that I personally find most interesting. Funny how that works out.
We’ll start in the ocean, which is full of weird animals that no human has ever seen before. It’s about a hermit crab who carries a friend around. The hermit crab was already known to science, but until a team of scientists observed it in its natural habitat, the deep sea off the Pacific coast of Japan, no one realized it had an anemone friend.
The sea anemone is related to jellyfish and is a common animal throughout the world’s oceans. Some species float around, some anchor themselves to a hard surface. Many species have developed a symbiotic relationship with other animals, such as the clownfish, which is sometimes called the anemonefish because it relies on the anemone to survive. Anemones sting the way jellyfish do, but it doesn’t sting the clownfish. Researchers aren’t sure why not, but it may have something to do with the clownfish’s mucus coating. Specifically, the mucus may have a particular taste that the anemone recognizes as belonging to a friend. If the anemone does accidentally sting the clownfish, it’s still okay because the fish is generally immune to the anemone’s toxins.
The clownfish lives among the anemone’s tentacles, which protects it from predators, and in return its movements bring more oxygen to the anemone by circulating water through its tentacles, its droppings provide minerals to the anemone, and because the clownfish is small and brightly colored, it might even attract predators that the anemone can catch and eat.
Anemones also develop mutualistic relationships with other organisms, including a single-celled algae that lives in its body and photosynthesizes light into energy. The algae has a safe place to live while the anemone receives some of the energy from the algae’s photosynthesis. But some species of anemone have a relationship with crabs, including this newly discovered anemone.
The anemone anchors itself to the shell that the hermit crab lives in. The crab gains protection from predators, who would have to go through the stinging tentacles and the shell to get to the crab, while the anemone gets carried to new places where it can find more food. It also gathers up pieces of food that the crab scatters while eating, because crabs are messy eaters.
The problem is that hermit crabs have to move into bigger shells as they grow. Anemones can move, but incredibly slowly. Like, snails look like racecar drivers compared to anemones. The anemone moves so slowly that the human eye can’t detect the movement.
What the team of scientists witnessed was a hermit crab spending several days carefully pushing and pinching the anemone to make it move onto its new shell. If it wasn’t important, the crab wouldn’t bother. The sea anemone hasn’t yet been officially described since it’s still being studied, but it appears to be closely related to four other species of anemone that also attach themselves to the shells of other hermit crab species.
In other marine invertebrate news, a researcher named Jeff Goddard was turning rocks over at low tide at Naples Point, California a few years ago. He was looking for sea slugs, but he noticed some tiny clams. They were only about 10 mm long, but they extended a white-striped foot longer than their shells. Goddard had never seen anything quite like these clams even though he was familiar with the beach and everything that lived there, so he took pictures and sent them to a clam expert. The expert hadn’t seen these clams before either and came to look for the clams in person. But they couldn’t find the clams again. It took ten trips to the beach and an entire year before they found another of the clams.
They thought the clam might be a new species, but part of describing a new species is examining the literature to make sure the organism wasn’t already described a long time ago. Eventually the clam research team did find a paper with illustrations of a clam that matched, published in 1937, but that paper was about a fossilized clam.
They examined the 1937 fossil shell and compared it to their modern clam shell. It was a match! But why hadn’t someone else noticed these clams before? Even Goddard hadn’t seen them, and he’s a researcher that spends a lot of time along the coast looking specifically for things like little rare clams. Goddard thinks the clam has only recently started extending its range northward, especially during some marine heatwaves in 2014 through 2016. He suspects the clam’s typical range is farther south in Baja California, so hopefully a future expedition to that part of the Pacific can find lots more of the clams and we can learn more about it.
We talked about deep-sea isopods just a few weeks ago, in episode 311. They’re crustaceans related to crabs and lobsters, but also related to roly-polies that live on land. The deep-sea species often show deep-sea gigantism and are referred to as giant isopods, and that’s what this newly discovered species is. It was first found in 2017 in the Gulf of Mexico and is more slender than other giant isopods. The largest individual measured so far is just over 10 inches long, or 26 cm, which is almost exactly half the length of the longest giant isopod ever measured. It’s still pretty big, especially if you compare it to its roly-poly cousins, also called pillbugs, sow bugs, or woodlice, who typically grow around 15 mm at most.
Before we get out of the water, let’s talk about one more marine animal. This one’s a mystery that I covered in the October 2022 Patreon episode. It was suggested by my brother Richard, so thank you again, Richard!
On August 30, 2022, a research team was off the coast of Puerto Rico, collecting data about the sea floor. Since the Caribbean is an area of the ocean with high biodiversity but also high rates of fishing and trawling, the more we can learn about the animals and plants that live on the sea floor, the more we can do to help protect them.
When a remotely operated vehicle dives, it sends video to a team of scientists who can watch in real time and control where the rover goes. On this particular day, the rover descended to a little over 1,300 feet deep, or around 407 meters, when the sea floor came in view. Since this area is the site of an underwater ridge, the sea floor varies by a lot, and the rover swam along filming things and taking samples of the water, sometimes as deep as about 2,000 feet, or 611 meters.
The rover saw lots of interesting animals, including fish and corals of various types, even a fossilized coral reef. Then it filmed something the scientists had never seen before. It was a little blue blob sitting on the sea floor.
The blue blob wasn’t moving and wasn’t very big. It was shaped roughly like a ball but with little points or pimples all over it and a wider base like a skirt where it met the ground, and it was definitely pale blue in color.
Then the rover saw more of the little blue blobs, quite a few of them in various places. The scientists think it may be a species of soft coral or a type of sponge, possibly even a tunicate, which is also called a sea squirt. All these animals are invertebrates that don’t move, which matches what little we know about the blue blob.
The rover wasn’t able to take a sample from one of the blue blobs, so for now we don’t have anything to study except the video. But we know where the little blue blobs are, so researchers hope to visit them again soon and learn more about them.
It wouldn’t be a newly discovered species list without at least one new frog. Quite a few frogs were discovered in 2022, including a tree frog from Vietnam called Khoi’s mossy frog. It lives in higher elevations and is pretty big for a tree frog, with a big female growing over 2 inches long, or almost 6 cm, from snout to vent. Males are smaller. It’s mostly brown and green with little points and bumps all over that help it blend into the moss-covered branches where it lives. That’s just about all we know about it so far.
Our next discovery is an invertebrate, a spider that lives in bamboo. Specifically it lives in a particular species of Asian bamboo in Thailand, and when I say it lives in the bamboo, I mean it really does live inside the bamboo stalks. Also, when I say it’s a spider, specifically it’s a small tarantula.
It was first discovered by a YouTuber named JoCho Sippawat, who travels around his home in Thailand and films the animals he sees. I watched a couple of his videos and they’re really well done and fun, and he’s adorable even when he’s eating gross things he finds, so I recommend his videos even if you don’t speak the language he speaks. I’m not sure if it’s Mandarin or another language, and I’m not sure if I’m pronouncing his name right either, so apologies to everyone from Thailand for my ignorance.
Anyway, Sippawat found a tarantula where no tarantula should be, inside a bamboo stalk, and sent pictures to an arachnologist. That led to a team of scientists coming to look for more of the spiders, and to their excitement, they found them and determined right away that they’re new to science. It was pretty easy to determine in this case because even though there are more than 1,000 species of tarantula in many parts of the world, none of them live in bamboo stalks. The new spider was placed in a genus all to itself since it’s so different from all other known tarantulas.
It’s mostly black and dark brown with narrow white stripes on its legs, and its body is only about an inch and a half long, or 3 1/2 cm. It can’t make holes into the bamboo plants itself, so it has to find a hole made by another animal or a natural crack in the bamboo. It lines its bamboo stalk with silk to make a little home, and while there’s a lot we don’t know yet about how it lives, it probably comes out of its home to hunt insects and other small animals since tarantulas don’t build webs.
Finally, let’s wrap around to the sea anemone again, at least sort of. If you remember episode 129, we talked about the Venus flytrap sea anemone, which is an animal that looks kind of like a carnivorous plant called the Venus flytrap. We then also talked about a lot of other carnivorous plants, including the pitcher plant. Well, in 2022 a new species of pitcher plant was discovered that has underground traps.
The pitcher plant has a type of modified leaf that forms a slippery-sided pitcher filled with a nectar-like liquid. When an insect crawls down to drink the liquid, it falls in and can’t get out. It drowns and is dissolved and digested by the plant. Almost all known carnivorous plants are pretty small, but the largest are pitcher plants. The biggest pitcher plant known is from a couple of mountains in Malaysian Borneo, and its pitchers can hold over 2 ½ liters of digestive fluid. The plant itself is a messy sort of vine that can grow nearly 20 feet long, or 6 meters. Mostly pitcher plants just attract insects, especially ants, but these giant ones can also trap frogs, lizards, rats and other small mammals, and even birds.
The newly discovered pitcher plant grows in the mountainous rainforests of Indonesian Borneo and is relatively small. Unlike every other pitcher plant known, its pitchers develop underground and can grow a little over 4 inches long, or 11 cm. Sometimes they grow just under the surface, with leaf litter or moss as their only covering, but sometimes they grow deeper underground. Either way, they’re very different from other pitcher plants in other ways too. For one thing, scientists found a lot of organisms actually living in the pitchers and not getting eaten by the plant, including a new species of worm. Scientists aren’t sure why some animals are safe in the plant but some animals get eaten.
The new pitcher plant is found in parts of Indonesian Borneo that’s being turned into palm oil plantations at a devastating rate, leading to the extinction or threatened extinction of thousands of animal and plant species. The local people are also treated very badly. Every new discovery brings more attention to the plight of the area and makes it even more urgent that its ecosystems are protected from further development. The fastest way to do this would be for companies to stop using so much palm oil. Seriously, it’s in everything, just look at the ingredients list for just about anything. I try to avoid it when I’m grocery shopping but it’s just about impossible. I didn’t mean to rant, but the whole palm oil thing really infuriates me.
You know what? Let’s have one more discovery so we don’t end on a sour note.
A biodiversity survey of two of Australia’s marine parks made some really interesting discoveries in 2022. This included a new species of hornshark that hasn’t even been described yet. It’s probably related to the Port Jackson shark, which grows to around five and a half feet long, or 1.65 meters, and is a slow-moving shark that lives in shallow water off the coast of most of Australia. Instead of a big scary mouth full of sharp teeth, the Port Jackson shark has a small mouth and flattened teeth that allow it to crush mollusks and crabs. The newly discovered shark lives in much deeper water than other hornsharks, though, around 500 feet deep, or 150 meters.
Another thing they found during the survey wasn’t a new species of anything, but it’s really cool so I’ll share it anyway. It was a so-called shark graveyard over three miles below the ocean’s surface, or 5400 meters. The scientists were trawling the bottom and when they brought the net up to see what they’d found, it was full of shark teeth–over 750 shark teeth! They were fossilized but some were from modern species while some were from various extinct species of shark, including a close relative of Megalodon that grew around 39 feet long, or 12 meters. No one has any idea why so many shark teeth are gathered in that particular area of the sea floor.
You can find Strange Animals Podcast at strangeanimalspodcast.blubrry.net. That’s blueberry without any E’s. If you have questions, comments, or suggestions for future episodes, email us at strangeanimalspodcast@gmail.com. If you like the podcast and want to help us out, leave us a rating and review on Apple Podcasts or Podchaser, or just tell a friend. We also have a Patreon at patreon.com/strangeanimalspodcast if you’d like to support us for as little as one dollar a month and get monthly bonus episodes.
Thanks for listening!